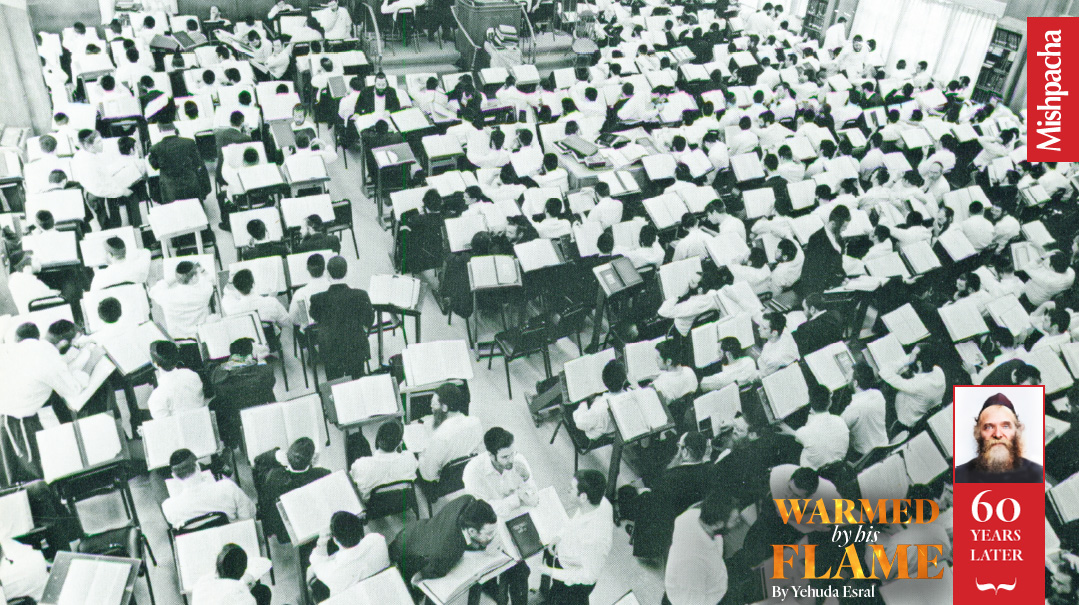
With Fire in His Eyes: The Burning Mission of Rav Aharon Kotler
| December 20, 2022Rav Aharon Kotler inspired a Torah revolution on three continents — but that’s just part of the story

Photos: BMG Archives, Agudah Archives, DMS Yeshiva Archives, Wolfson Family, Hoberman Family, Kamenetsky Family, National Library of Israel, US Dept of State, Prof. Chaim I. Waxman, YIVO, Torah Umesorah Archives, Chinuch Atzmai Archives, Perr Family, Golding Family, Bunim Family, TAJ Art and Judaica, Feivel Schneider
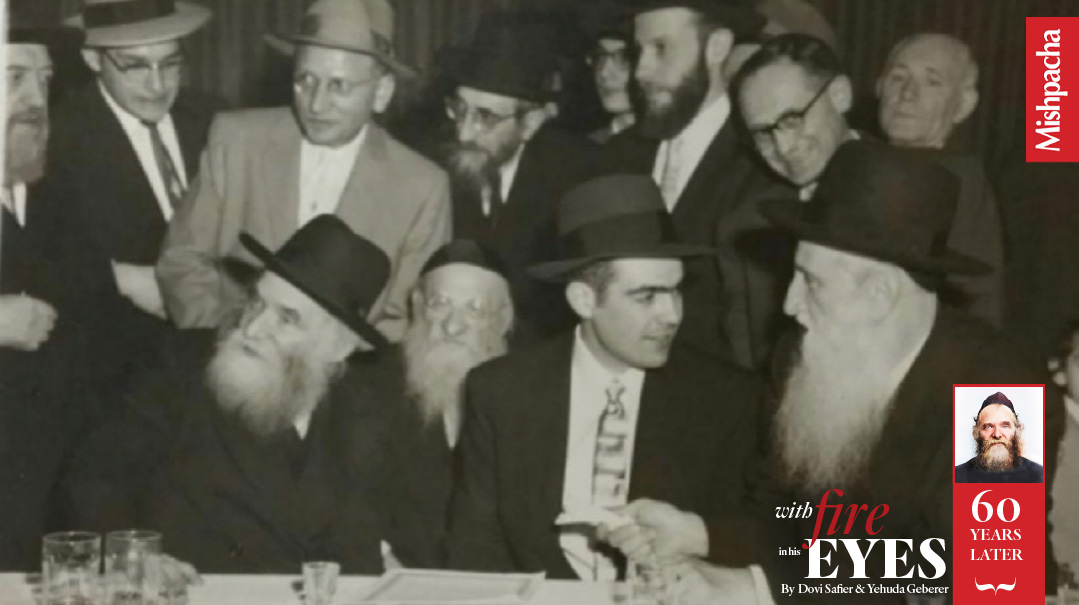
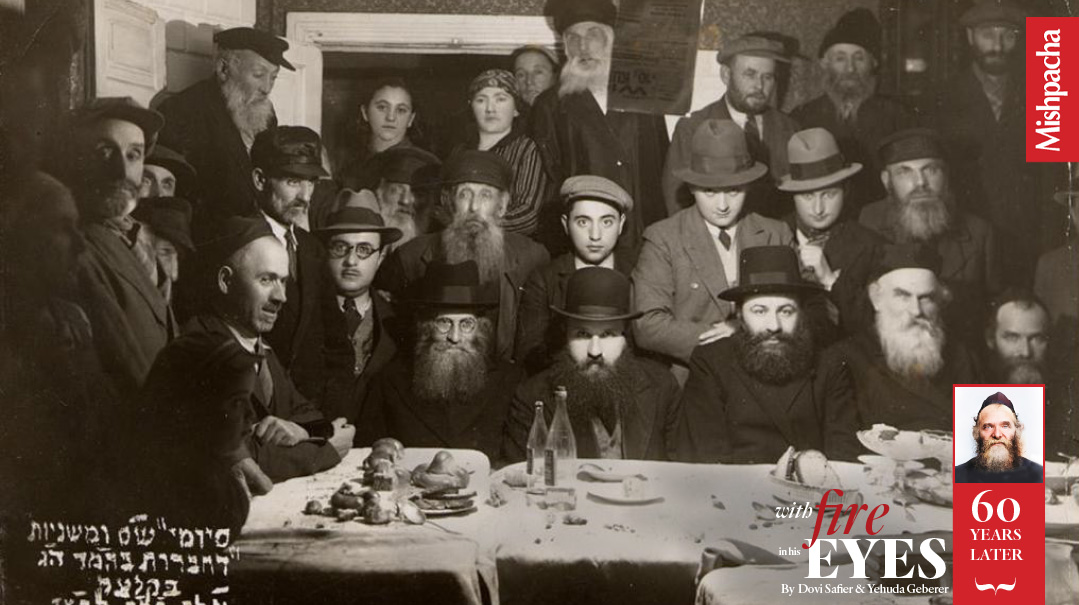
Boro Park, Brooklyn, late 1950s
A child is playing outside a shul. He is approached by a Mirrer talmid who spent the war years in Shanghai. The man asks him incredulously, “How can you play outside when Rav Aharon Kotler is delivering a shiur? How can you lose your chance to hear him speak?”
The boy obligingly goes inside and listens, not understanding a single word.
Decades later, he still recalled the scene: “I saw an older man speaking with a passion I had never seen before or since. His face was beet-red with excitement and exertion. His flaming blue eyes bore into the souls of all present. The energy he exuded, the pathos of his speech, and the glow of his face made it a surreal experience. Despite not having understood, that image is engraved in my mind for eternity.”
Such was an encounter with Rav Aharon Kotler.
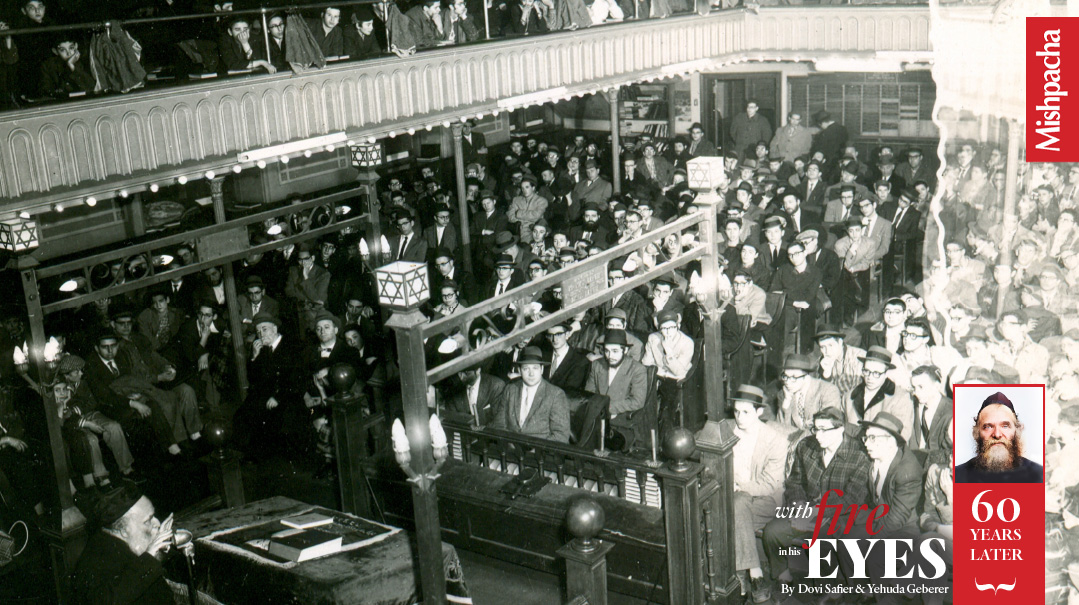

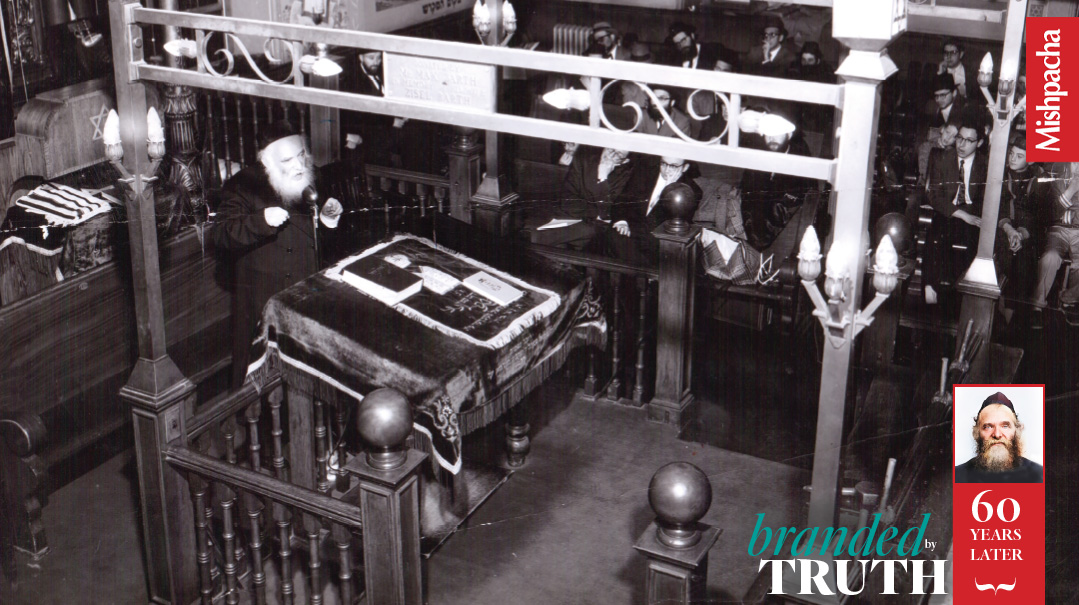
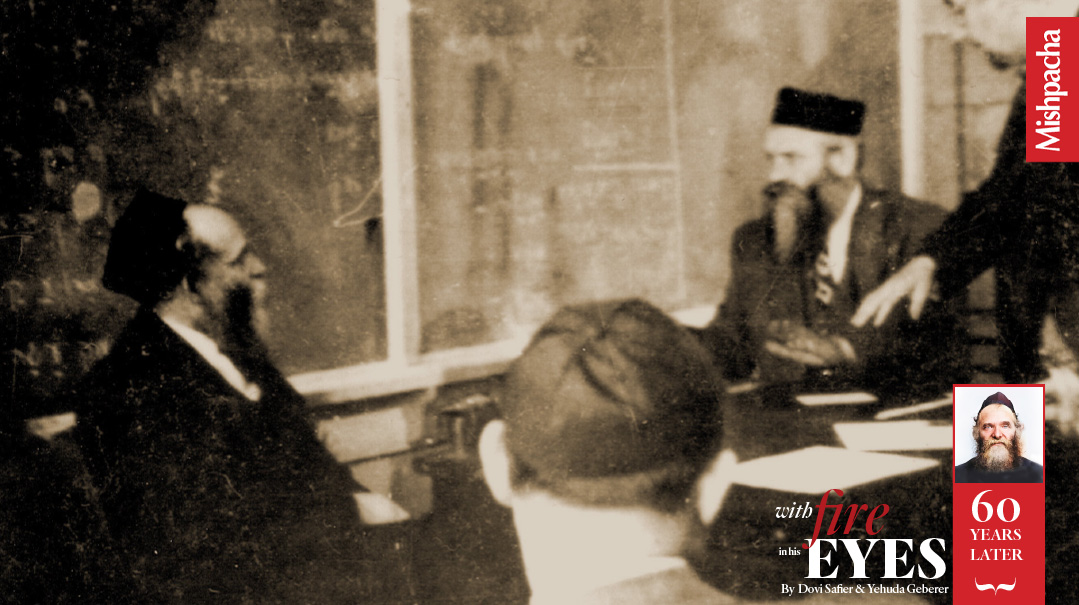
Rav Aharon delivering a shiur at the Bialystoker Synagogue on New York’s Lower East Side
Rav Aharon was the Rabban Yochanan Ben Zakkai of his time, tasked with picking up the pieces after the staggering destruction of the Holocaust. With penetrating vision and powerful determination, he inspired a Torah revolution on three continents — but that’s just part of the story.
For more than 20 years prior to his arrival in America, Rav Aharon Kotler was one of the leaders of Torah Jewry in Europe, standing alongside fellow gedolim a generation older than he. Even then, he displayed a sense of concern and responsibility for the wider Torah world, taking initiative and accepting burdens far beyond his own yeshivah. That wide-lens view accompanied him throughout his life, marking him not only as the Rosh Yeshivah who transformed America’s relationship with Torah learning, but as the leader who burned with a constant urgency to rescue, restore, initiate, rally, and support the growth of Torah wherever Jews could be found.
IT was the spring of 1941, and a small crowd gathered at a little shul on Clinton Street on the Lower East Side of New York. Rav Aharon Kotler, rosh yeshivah of the famous Kletzk yeshivah, had recently arrived in the United States, and they’d come to hear him speak — as much out of pity and respect as out of ideology.
The attendees were an assemblage of senior yeshivah students from NewYork yeshivos such as Torah Vodaath, Rabbeinu Yaakov Yosef (RJJ), and acouple of others. The rosh yeshivah was alone, separated from his students —albeit not for lack of trying to bring them to safety. He had recently met withAgudath Harabonim emissary Dr. Samuel Schmidt in Yanova, Lithuania, wherehis yeshivah had relocated. Rav Aharon pleaded with Schmidt to help arrangea transfer of the fragmented Lithuanian yeshivah world to the United States.
But it was not to be. Just weeks after Rav Aharon’s arrival in Americaon Erev Pesach of 1941, the Nazis invaded Soviet-occupied Lithuania andbrought an end to the golden age of Torah study in Eastern Europe. Most ofthe Kletzk students, the rest of the yeshivos, the masses of Lithuanian Jews, and communities across Eastern Europe would bemartyred in the Nazi carnage of the coming years.
On that day in 1941, Rav Aharon described thechain of Torah that commenced at Har Sinai andwas composed of links of various quality — someof precious metals and others of baser materials.He described the historical sequence of thetransmission of Torah from Rabban Yochanan benZakkai through the Rishonim and finished withrecent Torah leaders: Rav Chaim Brisker, Rav MeirSimchah of Dvinsk, and Rav Chaim Ozer Grodzinski.Reaching a fevered pitch, he began his plea, urgingthe assembled yeshivah students to forge anotherlink in the dynastic chain.
This was their introduction to Rav Aharon Kotler, and to his unbending assertion that there is only one way to produce Torah leaders of caliber: through channeling all the powers of one’s will and intellectual capacities toward the study of Torah. Without total submission to Torah learning, he said, without fundamental lomdus, toil and perseverance, Torah cannot takeroot in the individual’s soul, cannot change hisbeing or essence. There was no time or place fordistractions.
That historic talk articulated Rav Aharon’s ideology, mission, and contagious energy. It laid the groundwork for the establishment of Beth Medrash Govoha in Lakewood, and for a seismic change in America’s attitude toward Torah learning and living. Rav Aharon was never satisfied with words alone; this was a call for action. And act he did, with a fiery resolve that ignited a growing cadre of talmidim, activists, and supporters to act as well.
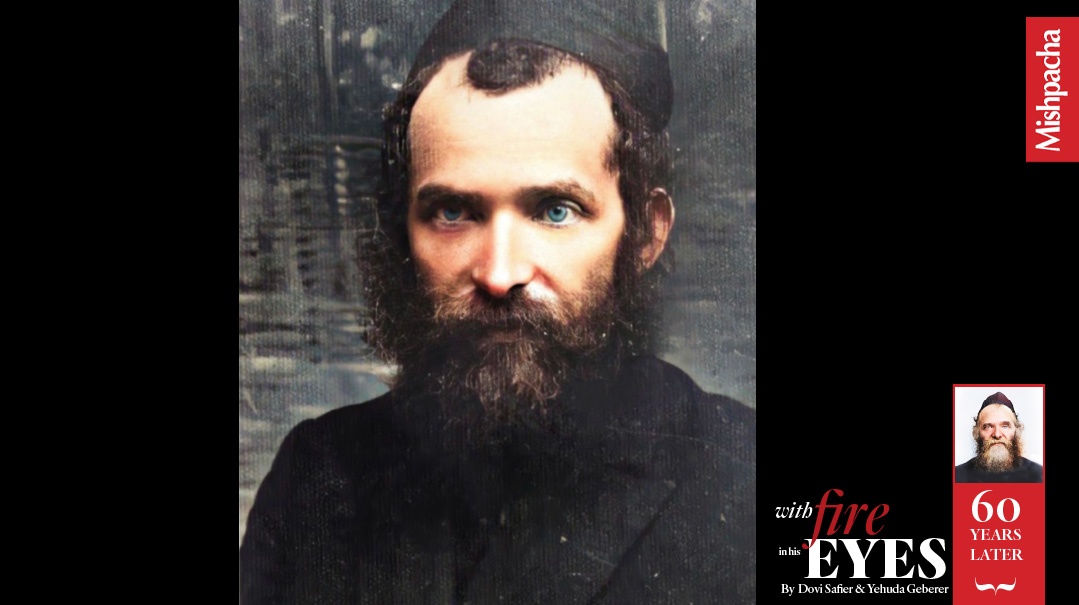

“Did you ever see the Rosh Yeshivah’s photograph? Do not accept it; for neither artist nor camera can capture the fire in his eyes, the radiance on his face, the exhilaration of his presence. The image engraved in one’s memory is more accurate than any photographic or artistic rendition. -Rav Shaul Kagan
Chapter One: Sunrise in Sislovitz
Son of Sislovitz
February 2, 1892 / the fourth of Shevat 5652. A day that lives in infamy in the annals of the yeshivah world.
Russian authorities shuttered the doors of the Volozhin Yeshiva, ending the nearly 90-year reign of the “mother of all yeshivos.” The prophetic words of Shlomo Hamelech promise that, “The sun rises and the sun sets.” The Gemara notes that in his formulation, the sun rises before it sets; a metaphor for the nhistory of Torah transmission. The Torah will begin to rise in a new place before its current locus goes dark.
The news of Volozhin’s closure spread quickly as students returned home to their respective cities and villages, among them the town of Śvisłač (Sislovitz), located 250 kilometers from Volozhin in Grodno Province, where a respected alumnus of the yeshivah, a rav named Rav Shneur Zalman Pines, was hosting a bris for his son, whom he named Aharon. “Zeh hakatan gadol yihyeh,” the mohelannounced. Little did anyone realize that the sun was beginning to rise onceagain, and few would play a larger role in lighting upthe dark sky than youngAharon.
Arke (as he was known) was born into a family that traced its lineage back to the Megaleh Amukos and Rashi. The name Pines was derived from the words, “al pines — by a miracle,” marking a miraculous salvation that took place generations prior.
Rav Shneur Zalman, the third son of Rav Moshe Pines, was born during the reign of Czar Nicholas I, when the dreaded Cantonist laws were in effect. In order to evade conscription, Rav Moshe obtained papers that named Shneur Zalman the only son of the Kotler family, thus exempting him from the draconian Czarist decree. While he reverted back to the prestigious Pines name later on in life, his son Arke would maintain the Kotler surname, and ensure that it would become a name enshrined with gold letters in the history of the Jewish nation.
Rav Shneur Zalman was described as “short, thin, and weak,” traits that young Arke inherited. But thankfully, he likewise inherited his father’s sharp mind and endless capacity to absorb knowledge, though it was his legendary diligence — an unusual intensity and zeal — that caused him to stand out among his peers.
Arke became the child prodigy of Śvisłač. One of his childhood friends later reminisced in the town’s Yizkor (memorial) book: “I would visit the house of the rabbi as a friend of the delightful child Arke (today Rav Aharon Kotler). We studied together with his father of blessed memory, and we spent many a mishmar (all-night learning session) together. The house of the rabbi shone with the splendor of(his son) the gaon. Arke was extolled for his sharp answers to the teachers’ questions.”
Another Śvisłač resident recalled that “the whole town marveled at how the Rav’s little boy could recite all of Tanach by heart.”
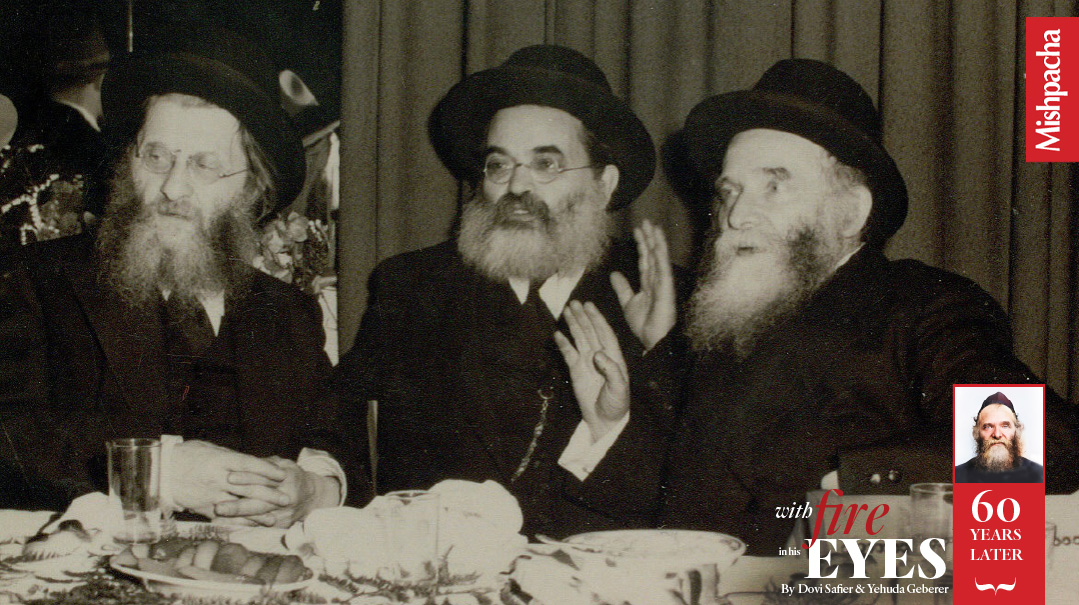

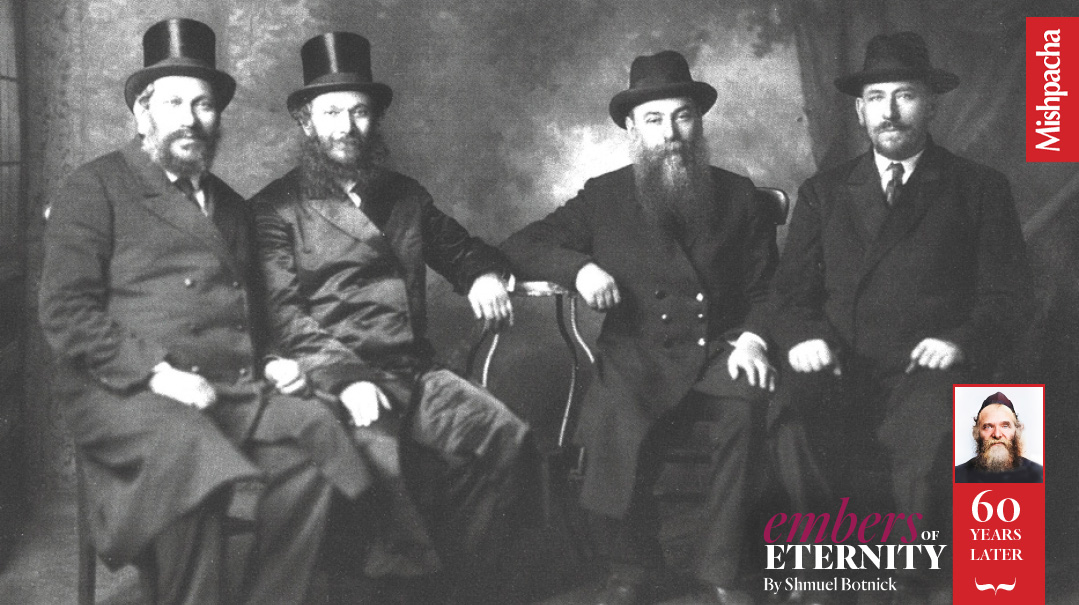
FRIENDS FOR LIFE: From their joint youth in Slabodka, through their common experience as talmidim of Slabodka, their traversing the Atlantic and eventually assuming positions in the rebuilding of the postwar Torah world, Rav Reuven Grozovsky with Rav Yaakov Kamenetsky & Rav Aharon shared destiny and leadership
Socialist Winds
Arke may have had a shining reputation, but his childhood was marred by tragedy and pain. He watched as those around him strayed from the faith their families had maintained for generations.
Most of the 2,000 Jewish residents in Śvisłač worked at local tanneries, which dominated the local economy. As the Jewish Socialist party, the Bund, began to make inroads in the region, workers began to organize and demand better salaries and working conditions. The Bund sought to organize the Jewish working class, and to remake Jewish identity as well, with Yiddish culture replacing religious observance. Oftentimes it wasn’t limited to mere abandonment of religion; it was openly hostile toward mitzvah observance.
Unfortunately, the trend toward socialism wasn’t limited to labor unions, and ambivalence toward religion soon turned into animosity. In his memoirs, Śvisłač resident David Lewis (later a leader in the Canadian Bund) described how soon after the onset of Shabbos, local youths would paste their leaflets to the door of the main shul in town, knowing that they couldn’t be removed by the Shabbos-observant attendees.
Cheder attendance began to dwindle, and in 1900a modern Hebrew school was opened. By 1915, a secular Yiddish school was dedicated in town, and within four years the cheder was shuttered.
Like most devout Jews in Śvisłač, Rav Shneur Zalman struggled to protect his children from the winds of change sweeping Eastern European Jewish youth. In 1896 his wife Sarah Pesha passed away and he was left to raise his children alone. His elder daughter Malka was ensnared by the secularist movements that captured the hearts and minds of the local youth. (While its unclear what became of his son Moshe, thankfully, his younger daughter Devorah was spared from this plague.)
A controversy erupted over the return of a former rabbi to town. Rav Shneur Zalman refused to take part in the polemics some were hurling at his opponent, but those close to him saw that he was suffering greatly. In 1903 he died suddenly, a death that many blamed on his pain over the upheaval. Young Aharon was left alone, bereft of both parents in a volatile world.
Two months later, following a short stay in Minsk, the 11-year-old orphan was sent by his uncle Rav Yitzchak Pines to study in the yeshivah in Krinik, under the leadership of Rav Zalman Sender Kahana- Shapiro, whom the Pines family was acquainted with from Volozhin.
In Krinik, Rav Aharon joined a seasoned group of older students, but had no difficulty keeping up and even standing out with his quick mind and impressive diligence. After studying for two zemanim in Krinik, Arke was ready to move on, and is said to have traveled to Slabodka where he joined Yeshivas Knesses Beis Yitzchak. The yeshivah was in the process of welcoming a new rosh yeshivah, Rav Baruch Ber Leibowitz, whose shiurim would dominate the Lithuanian Torah landscape for the next 35 years.
Back in 1897, a portion of the Slabodka student body revolted against the Alter of Slabodka’s educational approach. This soon escalated into an organized resistance to the mussar movement known as the “Pulmus Hamussar.” Ultimately, the Alter departed from his yeshivah and established Yeshivas Knesses Yisrael. He was followed there by the rosh yeshivah Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein and a few dozen loyal students. The majority of students, however, chose to remain with the Rav of Slabodka, Rav Moshe Danishevsky, until Rav Chaim Rabinowitz (known to posterity as Rav Chaim Telzer) was hired as rosh yeshivah.
In 1904 Rav Chaim Rabinowitz departed for Telz and was replaced by the rav of Halusk and a prime student of Rav Chaim Brisker, Rav Boruch Ber Leibowitz. Little is known about the time Rav Aharon spent at Knesses Beis Yitzchak, but the presence of the young student caused a stir in Slabodka, so much so that a plan was eventually put into motion to try and bring him to the Alter’s yeshivah, Knesses Yisrael.

Roots and Branches
Rav Zalman Sender Kahana-Shapiro
As a newly bereft orphan, young Aharon Kotler was sent to study in the yeshivah in Krinik, under the tutelage of Rav Zalman Sender Kahana- Shapiro.
One of the Torah giants of his time, Rav Zalman Sender was a great-grandson of Rav Chaim Volozhiner through his daughter Relkeh’s second marriage. In Volozhin he was a student of his cousin the Beis HaLevi, and was so attached to him that when the Beis HaLevi left Volozhin to assume the rabbinate of Slutzk in 1865, he joined him. In Slutzk he was paired with the Beis HaLevi’s son Chaim, who would soon light up the world as a young rosh yeshivah in Volozhin.
The story is told that the Beis HaLevi asked the two youngsters which was a bigger lamdan. “I can’t answer,” Rav Zalman Sender replied. “If I say I’m bigger, I’ll be a baal gaavah and if I say Rav Chaim is bigger, I’ll be a liar.”
Rav Chaim then riposted with glee, “I say that Zalman Sender is both!”
In addition to his spiritual prowess and unusually sharp mind, Rav Zalman Sender was musically talented and composed several niggunim that became mainstays in Lithuanian yeshivos. His nusach for Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur became popular as well. Rav Boruch Ber Leibowitz — also known for his musical gifts — shared how on Seder night, the townspeople of Krinik would gather outside Rav Zalman Sender’s window to hear him sing.
In 1885 he was appointed rabbi of Maltch. When Yeshivah Knesses Beis Yitzchak opened in Slabodka in 1898, Rav Zalman Sender was among those invited to become its rosh yeshivah (and according to one source, even spent a few days there). Community leaders in Maltch feared losing their rav, and offered to establish a yeshivah for him in town. Rav Zalman Sender accepted and shortly thereafter opened a yeshivah there. He named it Anaf (branch of) Etz Chaim after his alma mater of Volozhin. In doing so, he expressed his hope to pay tribute to his illustrious forebear, and to imply that his yeshivah was to be a resurrection of the “mother of all yeshivos” which had been shuttered several years prior.
Among his students were his brilliant son Rav Avrohom Dov Ber Kahana- Shapiro (the Dvar Avraham), Rav Yaakov Kamenetsky, Rav Yecheskel Sarna, Rav Avrohom Yaffen, Rav Isser Yehudah Unterman, and Rav Yehuda Levenberg (later rosh yeshivah of New Haven).
In 1903 he was offered the rabbinate of the larger town of Krinik, which he accepted on condition that he could open a yeshivah there as well. Rav Shimon Shkop replaced him in Maltch in both capacities.
During the first World War he fled eastward, eventually making his way toward the land of Israel where he settled in Yerushalayim until his passing in 1923.
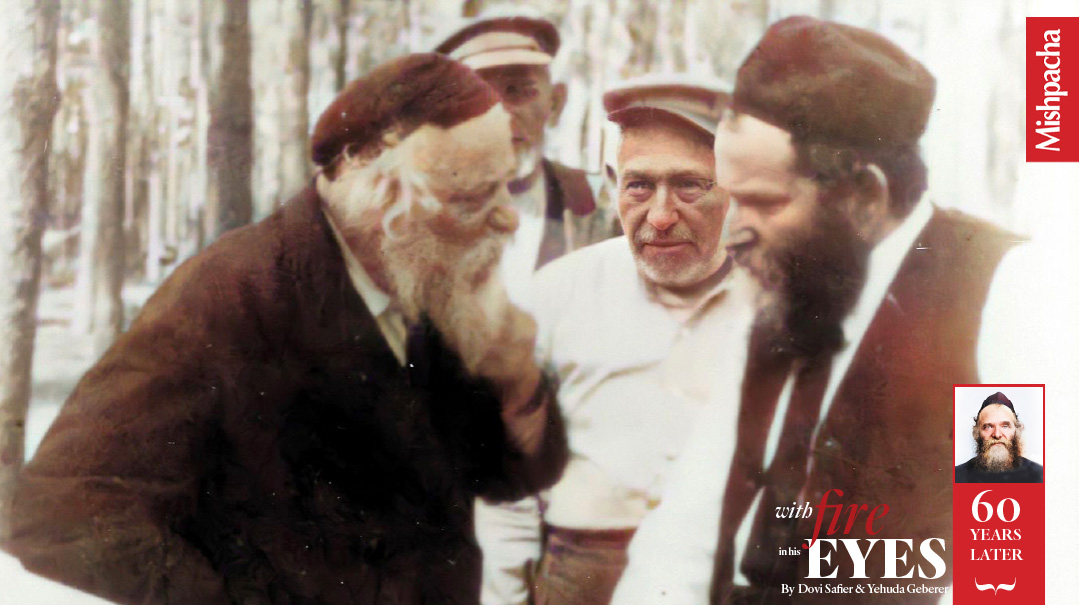


Rav Aharon and Rav Boruch Ber: They were once walking together and came to a door. Rav Aharon refused to enter until Rav Boruch Ber went first. Rav Boruch Ber wouldn’t hear of it. He locked his arm with Rav Aharon’s arm and they walked through the door together
The Boy in the Butcher’s Shul
Prior to Pesach of 1905, Rav Aharon journeyed to Minsk and joined a kibbutz of older talmidim at the Katzovisheh (Butchers’) Shul. Many of the more than 100 shuls in Minsk belonged to the various workers’ guilds common to urban life at the turn of the century. There were shuls for carpenters, shoemakers, tailors, milliners, water carriers, kehillah officials, and even rag-makers.
Some of these shuls hosted “kibbutzim,” small groups of young men that studied there. Local families belonging to the shul wouldtake responsibility for feeding the students and provided them with a modest monthly stipend. A handful of these improvised yeshivos became formal institutions and gained some renown, such as the famous “Blumka’s Kloiz” and a yeshivah run by Rav Shlomo Goloventzitz, which served as a feeder for Slabodka.
Rav Shmuel Charkover, rosh yeshivah of Bais Hatalmud, shared with his student Rav Michel Shurkin that as a 14-year-old, Rav Aharon penned a kuntres on Maseches Mikvaos that “dazzled the Torah world.” Minsk began to take notice of the young boy learning diligently in the Butchers’ Shul. In recognition of his status, as well as the fact that he was an orphan, Rav Aharon was provided by the Katzovisheh Shul with a significantly larger stipend than others.
In Minsk, Arke became acquainted with another budding Torah scholar just a few months his
senior named Yaakov Kamenetsky, with whom he developed a close relationship. Rav Yaakov, who wasn’t prone to hyperbole, later recalled his mother’s reaction upon meeting his friend: “Who is this boy? The Shechinah shines from him!”
Minsk’s spirit of Toras chesed was a tradition from the city’s great rabbinic leaders of the 18th century: Rav Leib Baal Hatosafos, his grandson Rav Aryeh Leib Gunzburg, the Shaagas Aryeh; and Rav Yechiel Halpern, the Seder Hadoros. Local rabbanim occasionally delivered shiurim to the students, but otherwise these improvised yeshivos generally lacked formal structure and authority. This arrangement presented an open door for the various ideological movements sweeping the increasingly radicalized Jewish street.
These tempting ideologies threatened to ensnare many of the day’s finest young Torah minds. A savior arrived in the form of Rav Reuven Grozovsky, an older student of the Alter of Slabodka. He sought out Arke out of concern for the potential adverse influence of the modern movements sweeping through Minsk.
Rav Reuven decided to ensure that Arke would be protected by bringing him to Slabodka where the great educator, the Alter of Slabodka, Rav Nosson Tzvi Finkel, could take him under his wing.
Even the trip from Minsk to Slabodka required planning; namely, a donor who would fund it. To appreciate this saga, we fast-forward a half-century to Tel Aviv, Israel:
In the mid-50s, Rav Mordechai Shapiro, a talmid of Rav Aharon Kotler ztz”l, traveled to Israel. One Erev Shabbos he saw a small kiosk in Tel Aviv, and someone asked the proprietor for a pack of cigarettes. The man looked up and asked, “Mah hashaah — what time is it?”
“Shteim-esrei v’chetzi — twelve-thirty,” came the answer.
“Well, I don’t sell cigarettes after chatzos on Erev Shabbos,” the man said.
That piqued Rav Mordechai Shapiro’s interest. His curiosity got the better of him, and he struck up a conversation.
“Shalom aleichem, what’s your name?”
“Yankele Ochsenkrug,” the proprietor said.
“Where are you from?” Rav Mordechai went on.
“Minsk. And where are you from?”
“America,” Rav Mordechai Shapiro answered.
“America. A Yid fun Amerike,” the man mumbled to himself. Years ago he knew a little child in Minsk, and he remembered giving money for this child’s ticket to Slabodka. Years later he heard that this child had somehow ended up in America and opened a yeshivah.
“Well, vos is zein nomen — what’s his name?” Rav Mordechai asked.
“Arke Sislovitzer,” replied the old man.
He explained that he used to be a butcher in Minsk, and he took a kopek from every ruble he made and put it aside to support Torah learning. There were a few precocious children in the shul there, and he paid for train tickets for two of them to go to Slabodka. He couldn’t remember the name of the other child, but this one he remembered, Arke Sislovitzer — he was a brilliant little child.
“Arke Sislovitzer is Rav Aharon Kotler,” Rav Mordechai told him. “He’s building Torah in
America!”
When Rav Mordechai returned home, he had the opportunity to speak at a Torah Umesorah convention, and was still taken by this story. He related the story about a poshute Yid who set aside a kopek from his earnings for hachzakas Torah. When he reached the punchline — Arke Sislovitzer, Rav Aharon Kotler! — there was suddenly a commotion at the head table. Rav Yaakov Kamenetsky stood up, walked over to Rav Mordechai and said, “I was the second child.”
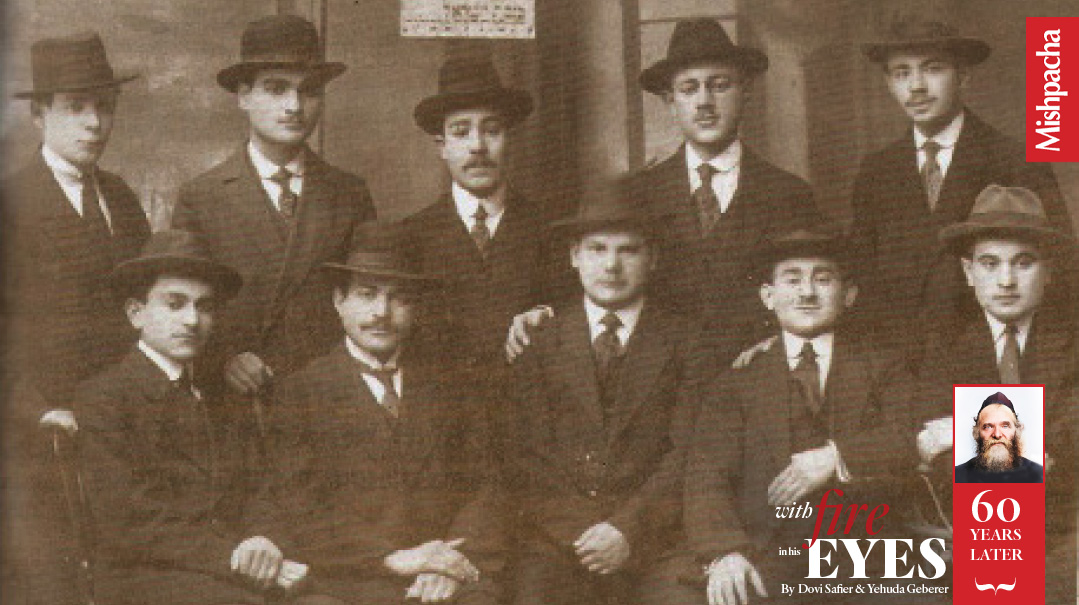

Rav Aharon as a student in Slabodka, seated second from left
Space in Slabodka
Following Pesach of 1906, Rav Aharon arrived in Slabodka together with RavYaakov. The following day the two were called in to the rosh yeshivah, Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein, for their entrance exam.
Rav Moshe Mordechai presented a section of the Ketzos Hachoshen and asked them to return with a challenge to the author’s discourse — which they succeeded in doing. They were then instructed to wait for the Alter to return from Kelm where he had spent Yom Tov with his family.
The following day saw the Alter’s return. He examined the two boys with his piercing eyes. After a short while, he informed them that the yeshivah was likely too crowded for the upcoming zeman. “Wait until all of the bochurim return,” he told them, “and perhaps there will be some space for you.”
Dejected, they exited the room. Fourteen-year-old Rav Aharon, however, noticed something amiss. After all, hadn’t they been “recruited” by a trusted student of the Alter? The Alter, in his genius, was likely testing their resolve. Without hesitating, Rav Aharon announced, “Why don’t we go study at the other yeshivah in town, (Knesses Beis Yitzchak)?”
The older student who was accompanying them quickly slipped away and reported what he’d heard to the Alter, who beamed with pride. They’d passed the test with flying colors. A few minutes later, they were offically welcomed into the yeshivah.
It didn’t take long for Arke Sislovitzer to be noticed. He was only 14 years old, but that didn’t stop him from being outspoken in shiur, challenging the rosh yeshivah, Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein. He was so short that he stood on a chair in order to be heard. The Alter cared for the neophyte as he would his own child, hosting him at his apartment adjacent to the yeshivah for Shabbos and Yom Yov meals alongside some of his closest older students.
In Slabodka there was something of a caste system, with older students rarely acknowledging their junior counterparts, let alone conversing with them. Most younger students were placed in the Ohr Hachaim Yeshivah Ketanah affiliated with Slabodka, known as Rav Hirschaleh’s yeshivah for its founder Rav Tzvi Hirsch Levitan. Rav Aharon’s immediate placement in the yeshivah proper awarded him unique status.
His stanzia (lodging place) was two blocks from the yeshivah, and the young teenager was often fearful to walk alone late at night. On occasion the Alter would accompany little Arke to his place of lodging. These efforts of the Alter to protect the young prodigy would pay dividends for generations to come — he would later say that it was worth maintaining the entire yeshivah with all of its hundreds of students if only to produce that one student, Arke Sislovitzer, who eventually became the great Rav Aharon Kotler.

The Vishker Illui, Rav Yaakov Safsel, was one of the great young prodigies of the Lithuanian Torah world at the turn of the century. At the wedding of Rav Shmuel Yitzchak Herman: Lower row: Rav Aharon Kotler, Rav Yaakov Safsel (Vishker Illui), Rav Shmuel Yitzchak Herman, Rav Avraham Kalmanowitz. Upper row behind the Vishker Illui is: Rav Avraham Trop. Rav Mordechai Elefant is to his left
In the Presence of Giants
The first months of Rav Aharon’s stay in Slabodka featured successive visits from great rabbinical leaders. He relished the opportunity to meet the aging Rav Dovid’l (Karliner) Friedman. When Rav Chaim Brisker passed through town, he commented that Rav Aharon closely resembled his father Rav Shneur Zalman Pines, who had been Rav Chaim’sstudent in Volozhin two decades prior.
When the Telzer rosh yeshivah, Rav Eliezer Gordon, arrived for a Shabbos in Kovno, the students of both Slabodka yeshivos crossed the bridge and converged upon his hotel. Years later in Baltimore, a former student at Knesses Beis Yitzchak, Mr. Harry Wolpert, described the scene: When Rav Leizer saw that hundreds of yeshivah students had arrived, he skipped the formalities and immediately launched into a shiurwith his trademark intensity. The studentslistened attentively until the flow was interrupted by a quiet but assertive voice. Who was the brave one?
Hundreds of eyes shifted their gaze towards Arke Sislovitzer. Almost as quickly as he’d been interrupted, Rav Leizer shot back, “Du ploiderst vi a shaigetz! — You babble like a shaigetz!”
That made it official. There was no longer any doubt that one of the youngest students in Slabodka was also one of its greatest, for there was nothing more complimentary in yeshivah circles than being the recipient of a full-frontal attack by the great Rav Leizer Telzer — who would regularly use barbs to buy time as his lightning-quick mind reworked his thought process.
(This proverbial rite of passage was adapted by many roshei yeshivah, Rav Aharon among them. When he delivered his shiur in Kletzk or Lakewood, it was often a challenge to follow his line of reasoning. If a student interrupted, he would yell at him, “Du redst vie a shikere Turk! — You’re speaking like an inebriated Turk!” i.e., you’re incomprehensible. And with that he’d proceed with the shiur.
Rav Shmaryahu Schulman once related a humorous incident. Rav Aharon would occasionally remark, “You know the shiur like you know Peking, China!”When some of the Kletzker students fled to China during the war, they’d quip, “Now at least we know China!”)
During Rav Aharon’s years at Knesses Yisrael, it was commonplace for elite students to go listen to Rav Boruch Ber Leibowitz’s shiurim at the rival yeshivah of Knesses Beis Yitzchak. Once the students of Knesses Beis Yitzchak locked the doors, preventing these students from entering. Rav Aharon wouldn’t be deterred and climbed in through the window to hear the shiur.
While Rav Aharon regularly attended shiurim of Rav Boruch Ber, he also considered himself a talmid of Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein, whose shiurim he attended as well. Apparently, he was studying two different masechtos in depth, simultaneously.
Saved by Rav Reuven
Even while seeing success at Slabodka, there were constant pressures from family members as well as the Jewish street to conform to the pressures of modernity.
Rav Aharon Kotler’s sister Malka was relentless in trying to convince him to leave Slabodka, enroll in university, and join the modern world. Sensing the detrimental effect a steady correspondence with his sister might have on his potential growth, the Alter initiated a dramatic step. He commissioned Rav Reuven Grozovsky with the unenviable task of censoring Rav Aharon’s mail.
Eventually, Rav Aharon discovered that his mail was being censored and became extremely upset, and decided to leave the yeshivah. As he headed to the Kovno railway station, the Alter was notified and rushed to the station (another version has him sending a student). There he persuaded Rav Aharon to return to Slabodka, and thus the future Torah leader was preserved.
At a memorial gathering held for Rav Reuven Grozovsky many years later, Rav Aharon Kotler rose to speak. He choked up, and remained crying at the podium for ten minutes without saying a word. Rav Yaakov Kamenetsky then rose and declared, “I will explain why the Kletzker Rosh Yeshivah feels the way he does.” He then proceeded to share their Slabodka experiences, how Rav Reuven played a crucial role in their transfer from Minsk to Slabodka, and how he looked after their welfare there. Rav Aharon himself once stated, “Rav Reuven pulled me out of many blottes (mires).”
(Rav Elazar M. Shach witnessed the efforts of the Alter to protect his endangered students, and described the effect that this defensive mode of chinuch had upon him. Rav Asher Bergman writes that when a young illui (later to become a renowned rosh yeshivah) arrived in Kletzk, Rav Shach encouraged him to stop smoking, not out of health concerns — which they weren’t aware of at the time — but rather to ensure that should he stray from the path, at least he wouldn’t smoke on Shabbos.)
During his years in Slabodka, Rav Aharon continued to grow in learning, while also integrating the mussar lessons of the Alter. After a certain point, the Alter no longer worried about Rav Aharon being influenced negatively and set out on another mission: to prepare Rav Aharon to be a Torah leader.
During one bein hazmanim intersession, Rav Aharon had the opportunity to speak in learning with Rav Meir Simchah of Dvinsk (the Ohr Sameach), who was taken with Rav Aharon and implored his teachers, “Take care of young Aharon, he has potential to emerge as a Rabbi Akiva Eiger of the generation.”
Fused to His Shtender
In 1938 the journalist Hirsch Movshowitz (under the pseudonym M. Gertz) shared memories of his time in Slabodka in the Riga-based Yiddish newspaper Haynt in an article entitled: “The Once-in-a Generation Gaon, HaRav Aharon Kotler,” excerpted below:
Thirty-two years ago, when I came to Yeshivas Slabodka, Knesses Yisrael had a number of bochurim that were renowned giants in Torah…
Among the younger group, there were three younger bochurim [known to be exceptional], they were almost yingerlach (children): The Vishker Illui, Hershke Semiatytcher, and last but not least Arke Sislovitcher.
The youngest of them all was Arke Sislovitcher, a child of 13 or 14. He was the synthesis of both previous illuyim. He was the charif and the baki, he had the sharp mind and the breadth — but primarily the sharpness.
He was quiet, calm, easygoing, a boy tender as silk, who spent day and night learning and serving the Creator. He and his shtender and the Gemara were so attached to one another, that aside from the fact that by his bar mitzvah he was already an exceptional illui, he was less noticeable than the other two, because he and the Gemara were fused together as one, from one skin.
Everyone knew that Arke Sislovitcher was artfully entitled by the lomdishe world with the words “tzaneh malei safra — a basket full of seforim.” And an “oker harim vetachnan zeh bazeh — one who uproots mountains and grinds them one against the other.”
Despite his young age, there was great respect for him because of his brilliance and hasmadah, and that’s why no one dared to go over to the illui to “speak to him in learning.” Because, first of all, it was too audacious to try to keep up with him in Torah. Second, because no one had the heart to tear the illui away from his Gemara, which he lapped up with hasmadah like a thirsty person from a spring of water.
It wasn’t in the nature of the Sislovitzer to allow his true brilliance to be heard. I remember just one time; we were together in Romshishuk for vacation. The principal of the Kovno Gymnasium found out that among the bochurim there was an illui — a wunderkind. The Russian principal was curious to test the genius of this boy in mathematics.
[He presented] complicated mathematical problems that would be hard for a licensed engineer to solve, and the Sislovitzer resolved them in no time. Pacing up and down in the little room, he quickly supplied the answers.
The Russian principal was astonished. Was it possible? How could it be that such a small boy, who in his life never even visited an elementary school, should, on his own, immediately solve complex problems? So he came back the next day, well prepared.
This time, he planned to ask the little genius such a hard mathematical “klutz kasha” that he would gape in confusion. But what is difficult for a Russian principal, was utterly simple and straightforward for an illui from Knesses Yisrael. The Sislovitzer paced up and down the room, l’havdil like a Slabodka bochur with a difficult question in the Gemara, spun his thumb and readily solved the difficult mathematical problem. From that point on, every day the principal would send the young genius fresh eggs, fruit and other vegetables.

Ads in the Poltava based Hamodia wished mazel tov to Rav Aharon and Chana Perel Meltzer upon their marriage
Chapter Two: Mantle of Leadership
Fourteen Trailblazers
In 1914, following a nearly two-year engagement, 22-year-old Rav Aharon married Chana Perel Meltzer, daughter of Rav Isser Zalman and Rebbetzin Baila Hinda Meltzer. The wedding was celebrated on 8 Adar, 1914 in Slutzk. Rav Elazar M. Shach related that only one of Rav Aharon’s friends from Slabodka attended the wedding, which was the norm in those days. The kallah’s brother, Rav Tzvi Yehuda Meltzer, recalled that Rav Aharon delivered a brilliant Torah discourse, followed by a breathtaking display by his close friend Rav Avraham Elya Kaplan, who repeated the pilpul flawlessly with brilliant rhymes and a melodious tune.


Frank’s Family Reunion: Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein (second from left) on a visit to America. To his left are his brothers-in-law, Rav Sheftel Kramer and Rabbi Pesach Frank. To his right is Rav Sheftel’s mechutan, Rabbi Avraham Yitzchak Schuchatowitz
The Story Behind the Shidduch
In 1914 the 22-year-old Rav Aharon married Chana Perel Meltzer, daughter of Rav Isser Zalman and Rebbetzin Baila Hinda Meltzer. The story of Rav Aharon’s shidduch was shared by famed journalist Rabbi Aaron Ben-Zion Shurin, who heard it from Rav Isser Zalman Meltzer while studying in Eretz Yisrael in the 1940s.
“Rav Isser Zalman told me that he’d long been aware of young Ahrele Sislovitzer, the prodigy of Slabodka, and had hopes of becoming his father-in-law one day. One day, a meshulach from Slabodka came to Slutsk and told Rav Isser Zalman about the young Aharon Kotler, describing him as ‘the lion of the chaburah.’ At that point, Rav Isser Zalman realized that the secret was out, as the collector was likely singing Rav Aharon’s praises to anyone who would listen.
“Rav Isser Zalman described to me how he rose from his chair, donned his peltz (fur coat), and informed his rebbetzin, ‘Baila Hinda, I must go finalize the shidduch immediately.’ He traveled to Slabodka and asked his brother-in-law Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein to arrange the match. The rest is history.”
Rebbetzin Baila Hinda’s father was Reb Shraga Feivel Frank, a student and devoted supporter of Rav Yisroel Salanter. He used his wealth to assist the nascent mussar movement by supporting the Slabodka Yeshivah and other mussar-linked institutions.
Reb Shraga Feivel’s youngest daughter Devorah Kramer recalled the eulogy delivered by Rav Yitzchok Elchonon Spektor, the Kovno Rav, at her father’s levayah. “Reb Shraga Feivel left instructions that no hespedim be delivered at his funeral. I would disobey his request but I am afraid of him!” With that he sat down, satisfied that he had both complied with the request and also conveyed his sense of reverence.
In marrying into the Meltzer/Frank family Rav Aharon merited a wife who had grown up in a home steeped in Torah, and solidified a connection with a family that was influential in the Torah landscape over the last century.
Prior to his passing, Reb Shraga Feivel Frank requested of his wife to ensure that their four daughters all married young men who were fully engaged in a life of Torah. Golda Frank fulfilled her promise, and took as sons-in-law, Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein, Rav Isser Zalman Meltzer, Rav Boruch Horowitz (rosh yeshivah of Slabodka) and Rav Sheftel Kramer (mashgiach of Slutzk and New Haven). Her descendants include the leadership of Chevron-Slabodka, Beth Medrash Govoha, Ner Israel, and other Torah institutions.
A story is told regarding the brothers-in-law. Following Rav Isser Zalman’s appointment as rosh yeshivah in Slabodka, the Alter wished to hire Rav Aharon Bakst as an additional rosh yeshivah. A talmid of Volozhin, Slabodka and Kelm, Rav Archik served as rabbi of many cities over the course of his long career, including Siemiatycze, Tsaritsyn (Stalingrad), Shadova, Poltava, Suvalk, Lomza, and Shavli, and a few others. In most instances he established and served at the helm of a local yeshivah as well. He and his family were martyred during the Holocaust.
There was, however, a problem. Rav Archik had once been engaged to one of the Frank daughters. The match had been broken off, because the family mistakenly perceived that Rav Archik desired to engage in the family business rather than embarking on the expected rabbinical career. Menucha Frank instead married Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein. When the Frank family heard that Rav Archik was the leading candidate for rosh yeshivah, they vehemently protested.
Rav Isser Zalman conveyed the Frank family’s position to the Alter of Slabodka, emphasizing the pain this was causing his mother-in-law, the elderly widow. The Alter then reconsidered Rav Archik’s appointment, and instead hired the Frank son-in-law Rav Moshe Mordechai as the second rosh yeshivah. With the founding of Slutzk Yeshiva in 1897, the Alter dispatched Rav Isser Zalman to be its rosh yeshivah, leaving Rav Moshe Mordechai the sole rosh yeshivah of Slabodka. That isn’t where the story ends, however.
Rabbi Shurin then added: “Rav Isser Zalman shared something personal with me. He said how, after he asked Rav Moshe Mordechai to serve as shadchan, a fleeting look crossed Rav Moshe Mordechai’s face and he realized that Rav Moshe Mordechai, who also had a daughter of marriageable age, had likely set his eye on him as well.
“‘Still,’ Rav Isser Zalman told me, ‘He didn’t say a word, or ever let on anything to that effect, and set out to make sure things went smoothly.’ Thus was the greatness of Rav Moshe Mordechai.”
Perhaps there was something else at play here. Two decades after Rav Isser Zalman spoke out on his behalf, Rav Moshe Mordechai finally had an opportunity to repay him by arranging the shidduch between Chana Perel and Rav Aharon.
(Nearly a century later, these two illustrious families came together once again when Rav Moshe Mordechai’s great-grandson, Rav Yosef Chevroni — current rosh yeshivah of Chevron-Slabodka — married Sarah Bakst, a great-granddaughter of Rav Archik.)

The new couple settled in Slutzk, where Rav Aharon soon joined the faculty of his father-in-law’s renowned Slutzk Yeshivah. The yeshivah had been founded in 1897 by the Alter of Slabodka at the behest of the rav of Slutzk, Rav Yaakov David Wilowski (the Ridbaz). Slutzk’s 10,000 Jews comprised more than 75 percent of the population. (The religious populace was predominantly non-chassidic, so much so that tradition had it included among what were said to be four exclusively misnagdic towns in the region, nicknamed “Karpas”: Kossovo, Ruzhinai, Pruzhan and Slutzk. Chassidic lore has it that Slutzk was “condemned” after the town mistreated the Baal Shem Tov.)
The rabbinate in Slutzk was one of the most prestigious in the region, having previously been held by Rav Yossel Peimer (Slutzker); the Beis Halevi, Rav Yosef Dov Halevi Soloveitchik; and later Rav Yechezkel Abramsky.
When the Alter acceded to the Ridbaz’s request and established a yeshivah in Slutzk, it was at great personal cost to his own yeshivah. In addition to sacrificing Rav Isser Zalman Meltzer, who was one of his roshei yeshivah in Slabodka, the Alter sent 14 of his finest students to Slutzk.
This group, known as the Yad Hachazakah, included future Torah leaders such as his son Rav Eliezer Yehuda Finkel, his son-in-law Rav Yehuda Leib Plachinsky, Rav Reuven Katz, Rav Alter Shmuelevitz, Rav Pesach Pruskin, Rav Moshe Yom Tov Wachtfogel, and Rav Yosef Konvitz.
Under Rav Isser Zalman’s leadership, the yeshivah emerged as one of the leading Lithuanian-style yeshivos in the Russian Empire. It was named Etz Chaim, presumably as an ode to Rav Isser Zalman’s alma mater in Volozhin.
Another member of the Yad Hachazakah, Rabbi David Rackman, who would later become a rav and businessman in Albany, described the joy exuded by the Ridbaz when he entered the beis medrash: “He would stand in the doorway virtually unseen and simply listen. Tears would well up in his eyes. He had re-sanctified a city by a simple relocation of 15 men!”
When the Ridbaz left Slutzk in 1903, the townspeople pressured Rav Isser Zalman to succeed him, and serve in the double capacity of communal rabbi and rosh yeshivah.
Prior to World War I the student body of the yeshivah had grown to more than 200, and Rav Isser Zalman embarked on a building campaign among Russia’s Jewish financial elite, culminating in the dedication of a building in 1912. In the interim he also hired a mashgiach, first Rav Shmuel Fundiler, then Rav Pesach Pruskin, and when the latter departed to establish his own yeshivah in Shklov, Rav Isser Zalman hired his brother-in-law Rav Sheftel Kramer for the position.
Luminaries who studied in Slutzk during its first two decades include Rav Elazar M. Shach, Rav Yosef Eliyahu Henkin, Rav Aryeh Levine, Rav Yaakov Kamenetsky, Rav Moshe Aharon Poleyoff, and Rav Moshe Feinstein. In addition to their regular shiurim, Rav Isser Zalman and Rav Aharon delivered halachah shiurim in hilchos Gittin and Choshen Mishpat to enhance the talmidim’s understanding of the relevant sugyos they were studying.
As the yeshivah grew, Rav Aharon’s own family grew as well. After losing a child in infancy, Rebbetzin Chana Perel gave birth to their son Chaim Shneur in 1918, followed by a daughter Sarah in 1921.
(Rav Shneur’s full name was actually Yosef Chaim Shneur. The name Yosef was added at age six when he contracted pneumonia, while Chaim was given together with Shneur because their firstborn, also named Shneur, had died in infancy. A Lithuanian tradition from the Vilna Gaon advised adding a prefix when using the name in the future. Another son, named Boruch Peretz after Rav Isser Zalman’s father, also died in infancy.)

At the behest of the Ridbaz, Rav Isser Zalman Meltzer led a group of 14 students from Slabodka to open a yeshivah in Slutzk
From Slutzk to Kletzk
Slutzk was one of the few yeshivos that didn’t endure exile during World War I, and continued to function in its original location under trying conditions of war and the subsequent Bolshevik Revolution and Civil War. When the final border was drawn between the Second Polish Republic and Soviet Russia in 1921, Slutzk found itself on the Soviet side, where the Yevsektsiya — Jewish section of the Communist Party — worked mightily to eradicate religious life.
The Yevsektsiya rightly recognized that Yiddishkeit could never coexist with Communism, and therefore aimed to destroy all institutions representing nationalism, culture and especially religion, from the traditional cheder and its melamed to the yeshivah and its dean. Their operatives held show trials and published newspapers “exposing” yeshivah students and teachers as counterrevolutionaries who were systematically poisoning the masses.
The faculty at Slutzk realized that the yeshivah would have to move away from Bolshevik sovereignty in order to continue operating, yet Rav Isser Zalman categorically refused to abandon his rabbinical responsibilities to his community. It was therefore decided to split the yeshivah. The older students would steal across the still-porous border led by the young and talented son-in-law of the rosh yeshivah, Rav Aharon Kotler. The younger students would remain with Rav Isser Zalman in Slutzk for the time being.
Rav Aharon successfully crossed the border into Poland and attempted to reestablish the yeshivah less than 40 miles away in Kletzk. The departure was painful, both for those who were leaving and those who remained in Slutzk. Reminiscing in Pinkas Slutzk, Rabbi Moshe Yissachar Goldberg, later a rav in New Orleans, described the painful scene:
“That winter day when the yeshivah was exiled from Slutzk to Kletzk is well preserved in my memory. It was after the treaty was signed between the Bolsheviks and the Poles, placing Slutzk under Soviet control. Rabbi Aharon Kotler shlita, his family, and some of the older students loaded their belongings onto a wagon and they themselves walked on foot, their heads bent and their hearts heavy.”
Crossing the border wasn’t just an escape from the anti-religious communists to the safety of Poland. It was also a symbolic — and no less daring — personal crossing for Rav Aharon.
Away from his illustrious father-in-law, Rav Aharon was now on his own. At 29 he was the youngest of Poland’s interwar roshei yeshivah, and he had now entered the public sphere as a rosh yeshivah, educator, leader and builder. The Torah world watched as its emerging leader proceeded to build one of the greatest yeshivos of the era.
Rav Aharon chose Kletzk partly as a result of its proximity to the new border, but there was a historical impetus as well. The town’s rav, Rav Chaim Shimon Herensohn, recalled that his father and predecessor had invited Slabodka to establish the branch there upon its founding in 1897. There was also a family connection as Rav Isser Zalman’s ancestors had previously been rabbanim of the town. The townspeople now welcomed Rav Aharon’s group of yeshivah students with open arms.
Rav Aharon immediately proved his leadership abilities. He promised the locals that he would pay for his students’ lodgings in what was then known as a stantzia arrangement. Their immediate needs were assumed by Rav Aharon, who had obtained a large quantity of saccharin as well as locally baked black bread. For two months the bochurim subsisted on sweetened water and black bread, with their diet supplemented on Shabbos when the townspeople hosted them for meals.

Rav Aharon at a town meeting in Kletzk (second row, third from left). The rav of Kletzk, Rav Chaim Shimon Herensohn, is on Rav Aharon’s immediate right.
Marketplace of Torah
Rav Mendel Krawiec, later rosh yeshivah of RJJ, recalled arriving for his entrance exam in Rav Aharon’s home in Kletzk: “The three-room apartment was sparsely furnished and was packed with yeshivah students who had come for their daily meal. Rav Aharon himself provided for many of the students in the early chaotic days. It didn’t have the appearance of a private residence. It was a bustling marketplace of Torah. Torah discussions filled the air, ideas debated, sugyos clarified. Amidst it all was the young rosh yeshivah guiding his students’ spiritual growth, while providing for their physical needs.”
Back in Slutzk, the remnants of the yeshivah were forced underground, and many talmidim, seeing no future under Soviet rule, crossed the border to Kletzk. The latter yeshivah’s numbers swelled as a result and by 1924 it contained 156 talmidim. Following a brief imprisonment by the Soviets, Rav Isser Zalman himself joined the yeshivah in Kletzk and resumed his former post as rosh yeshivah. But shortly thereafter, he immigrated to Eretz Yisrael where he assumed a position in the Etz Chaim Yeshiva in Yerushalayim. Once again, the growing yeshivah of Kletzk was left in the able hands of Rav Aharon.
One of the rebbeim alongside Rav Aharon was his close friend Rav Elazar Shach, who had married a niece of Rav Isser Zalman. Rav Shach remained in Kletzk through the early 1930s. (When Rav Shach assumed a position at one of the Novardok branches and later at the Karlin yeshivah in Luninitz, his family remained in Kletzk. Rav Shach would return home for the Yamim Tovim.) For the decade between 1925-35, Rav Yechezkel Levenstein served as mashgiach, and he was succeeded by Rav Yosef Leib Nenedik, who like his predecessor was a mussar product of the great Kelm Talmud Torah. He remained at his post as mashgiach of Kletzk through the onset of the Second World War, until he and his family were martyred along with most of the yeshivah students. Rabbi Yaakov Tcherbochovsky, husband of Rav Aharon’s sister Devorah, served on the yeshivah’s hanhalah as well. They too were martyred in 1941.
Rav Aharon’s focus on his studies was such that he regularly forgot to eat his meals. Rav Shaul Kagan, founder of the Pittsburgh Kollel, wrote that an older Kletzk student described how Rav Aharon once insisted on delivering the daily shiur despite a high fever. For more than two hours he stood and spoke with his usual fire and passion, occasionally pausing as he coughed up blood. “The aron was carrying its bearer,” the student aptly observed.
Rav Aharon was once in the midst of delivering a shiur in Kletzk during the snowy winter when the chimney became clogged. Soon the exhaust from the wood stove began to fill the beis medrash. Most of the students left until just a small group remained. When they felt themselves beginning to suffocate, one of them told Rav Aharon they couldn’t remain any longer. He answered, “That’s because you don’t understand the shiur. If you lived it, you wouldn’t feel the smoke!”
Public speaking, however, didn’t come naturally to Rav Aharon. Rav Shach once remarked, “You see the Rav Aharon of today, the dynamic leader. But I’ve known him since his youth. You might find it hard to believe he used to have terrible stage fright. Rav Aharon was once delivering a shiur in Kletzk when a stranger entered. Rav Aharon was overcome with stage fright because of the presence of one one unfamiliar person, so acute was his shyness. Clearly, one who accepts the responsibility of the nation’s leadership overcomes challenges beyond his nature.”

Rav Aharon (seated, far right) at a siyum in Kletzk
Groundbreaking Initiative
Rav Aharon was a forward-thinking leader who sought to establish the Kletzk Yeshivah on sound financial footing. So he hired a shadar — an official fundraiser, who in the case of Kletzk kept a full 50 percent of all earnings (a typical arrangement at the time). In 1924 this emissary was dispatched to Germany. A year later Rav Aharon complained that the system had failed to balance the yeshivah’s budget and noted in a letter that his monthly bread budget amounted to $300.
Even as the yeshivah’s deficit grew, the mashgiach, Rav Chatzkel Levenstein believed that the yeshivah needed its own building, and a building campaign was initiated. Rav Chatzkel’s daughter, Rebbetzin Zlata Ginsburg, recalled the exuberance of the Kletzk townspeople when they learned of this exciting development.
One by one, both men and women came forward with donations: money, bracelets, rings, silver pieces, gold pieces — just as during the building of the Mishkan, they offered whatever they had, and they didn’t stop there. Locals also volunteered to assist in its construction. Reb Shmuel Teitzmaller, whose family owned the local construction firm that built the yeshivah, described this exuberance decades later in a Beth Medrash Govoha newsletter:
“You could see a simple laborer or one of the balabatim grab a free moment, run over to the construction site, grab a few bricks and hand it to a bricklayer. All these Yidden wanted to save the yeshivah money, or to expedite the construction so that the building would be completed even faster — but most of all, everyone wanted some portion in this effort. They were all excited and willing to sacrifice… We would work from morning till night in the long summer days and not feel at all tired.”
Initially, the proud but small Kletzk community planned on supplementing the building fund through donations from the Kletzk Landsmanshaft communities in the United States. When this failed to produce the needed funds, Rav Aharon was forced to procure loans in order to complete the costs of the building. This further deepened the yeshivah’s deficit.
In order to generate publicity that would enhance fundraising prospects, Rav Aharon conceived the idea of a grand opening ceremony. With many rabbinic dignitaries in attendance, the festive Chanukas Habayis took place in the uncompleted building in November 1929. The special guest of honor was Rav Isser Zalman Meltzer, the former rosh yeshivah, who came all the way from Eretz Yisrael to savor his son-in-law’s accomplishments in his stewardship of the yeshivah. Upon seeing Rav Aharon after five years, Rav Isser Zalman said, “Er hut azoi fil geshtiggen (he grew so much), ich hub em nisht derkent (I didn’t recognize him)!”
The mutual respect between the two was immeasurable. Rav Aharon and his father-in-law once debated whether it was permissible for a short student to lend himself a taller appearance by inserting wooden slats in his shoes before meeting a potential shidduch prospect. Rav Isser Zalman believed the ploy was permitted, because he could retain that height by wearing the slats for the rest of his life. Rav Aharon theorized that the girl might think, “He’s a bit short, but if he were to insert slats in his shoes he’d appear taller,” therefore it would be considered deceitful. Rav Isser Zalman, who was a vaunted student of Rav Chaim Brisker and author of the Even Ha’ezel, marveled at the logic of his son-in-law.
(An interesting anecdote was related by Rav Aryeh Leib Grossnass. During his trip to Europe, Rav Isser Zalman visited the Chofetz Chaim in Radin. Rav Naftali Trop had recently passed away, and the students in Radin invited Rav Isser Zalman to deliver a shiur, after which they pleaded with him to remain as rosh yeshivah. They even locked the doors and incapacitated his waiting automobile to try and prevent his departure. Rav Isser Zalman then closeted himself in a room with the Chofetz Chaim to discuss the matter. Rav Grossnass relates, “Rav Isser Zalman left the room a half hour or forty-five minutes later, and I myself heard him saying, ‘I wouldn’t stay in Radin if I was paid all the money in the world, absolutely not!’ It turned out that the Chofetz Chaim had told him, ‘I envy you. You live in the Holy Land and serve as a rosh yeshivah. You will live for many years in Eretz Yisrael; HaKadosh Baruch Hu will yet help you, and in Eretz Yisrael you will come up with great chiddushei Torah.’
“‘After hearing such things from the Chofetz Chaim,’ Rav Isser Zalman declared, ‘I wouldn’t stay here for all the money in the world! I fully believe that whatever comes out of the Chofetz Chaim’s mouth is prophecy. It’s simply not worth it for me to stay here and miss out on such blessings.’”)
The Chanukas Habayis in Kletzk was an impressive event that enhanced the yeshivah’s prestige. After hovering at around 150 talmidim for several years, the yeshivah experienced a growth spurt in the early 1930s and by 1932 counted 230 talmidim. Rav Aharon proudly wrote to Rav Yosef Shub of the Vaad HaYeshivos that “aside from Mir and Radin, there is no yeshivah (in that region of Poland where most yeshivos were located) larger than ours.”
As the yeshivah grew in size, Rav Aharon worked to ensure it grew in quality as well. Rav Noach Bornstein, later one of the great students of the Brisker Rav, studied in Kletsk before transferring to Mir. Rav Beinush Finkel shared that on the day that Rav Noach left for Mir, Rav Aharon was absent from the yeshivah. When he returned and found him gone, he hastened to Mir with the intention of bringing back his treasured student.
The Mir rosh yeshivah, Rav Eliezer Yehuda Finkel, understood that if Rav Aharon was exerting such energy to retrieve Rav Noach, then he must be worth keeping, and so argued that he already belonged to Mir. Rav Noach himself was questioned as to his preference — to which he responded softly that had he wanted to stay in Kletzk, he never would have come to Mir.
Rav Aharon’s shiurim gained renown during the Kletzk era, and he came to be known as a great charif, a sharp and incisive thinker. Erupting in torrents of thought like a volcano, he’d cite a tradition from Rav Yisrael Salanter that “Torah is studied with venom, not with calm equanimity or coldness and apathy.” He spoke quickly. He was excitable. The in-depth analysis delivered in a staccato tone presented an intellectual challenge requiring full concentration. Rav Aharon Leib Steinman, who studied in Kletzk for a short time, described how Rav Aharon would move from one concept to another with lightning speed, requiring 100 percent focus in order to keep pace.
Following the shiur, a review was conducted by a gifted student named Pesach Horowitz and later by Shmuel Maslow, the latter of whom it was said would repeat the entire shiur without adding a single explanatory word or comment. One talmid recalled how Shmuel would recall precisely at which point Rav Aharon had cleared his throat during the shiur.

Strength in Unity
By 1924 the desperate financial straits of the yeshivos in the region led to the founding of one of the most unique organizations in the annals of the yeshivah world: the Vaad HaYeshivos.
The Vaad HaYeshivos, which was the brainchild of the Chofetz Chaim, would serve as an umbrella organization for the fundraising and budgeting operations of all member yeshivos. Under the direction of Rav Chaim Ozer and several of the leading roshei yeshivah of the 1920s, the Vaad HaYeshivos oversaw a fundraising and distribution apparatus that attempted to somewhat alleviate the burden sustained by each individual institution.
Though its focus was always financial, the Vaad ventured into other areas of yeshivah and even communal activity, including printing seforim, placement of applicants, and publishing its own newspaper.
Rav Aharon took an active and eventually leading role. He served, along with Rav Shimon Shkop and Rav Eliezer Yehuda Finkel, as one of the triumvirate of the Vaad Hapoel (executive board), which is quite astounding considering his relative age. In this capacity he maintained a very active correspondence with the two tireless administrators of the Vaad HaYeshivos in Vilna — Rav Yosef Shub and Rav Aharon Berek.
The Vaad HaYeshivos attempted to centralize fundraising efforts on behalf of the yeshivos within the Kresy region. To that end, pushkes were distributed to shuls and private homes, a publicity campaign was launched to encourage the public to donate in the local pushkes, and gabbaim were hired to oversee operations in each locality and empty the pushkes at regular intervals.
In a 1928 letter to the askanim in the field engaged in the pushke operation, Rav Aharon and his fellow roshei yeshivah of the Vaad Hapoel laid down precise instructions:
“Our experience shows us that if the pushkes are emptied more frequently, then donations are more frequent and at regular intervals. The donations are larger and the cause remains on their minds as a result as well.”
With the onset of the worldwide financial crisis and the Great Depression in 1929, the yeshivos found themselves in ever more dire financial straits. In sheer desperation, some yeshivos decentralized by engaging in local fundraising in Poland, which was against the regulations of the Vaad HaYeshivos. As a rosh yeshivah himself, Rav Aharon understood the predicament and advised the Vaad to look the other way, in a letter to Vaad secretary Rav Yosef Shub in 1933:
“You understand that at this point individual fundraising is now viewed as permissible. It is well-known for quite a while that yeshivos are engaging in decentralized fundraising based on their individual needs. We discussed this issue at a recent meeting, and it was decided that due to the current distressing financial situation there is nothing that should be done to prevent them from doing so.”
The poverty they faced was on display in another letter to Rav Yosef Shub where Rav Aharon urged, “to give on our account to the bochur, Chaim Yehonasan, 50 volumes of Gemara Kiddushin, which are needed urgently. The rest, approximately 80, will be given to us by the Vaad HaYeshivos, as they promised that they would be ready right after the holiday.” At the bottom of the letter Rav Aharon adds a note saying, “Perhaps the bookstore will accept a note from the Vaad promising payment shortly.”

Rav Aharon’s approach to communal leadership was the same as his approach to Torah study: the establishment of firm principles, broadness of scope and a most detailed conclusion.
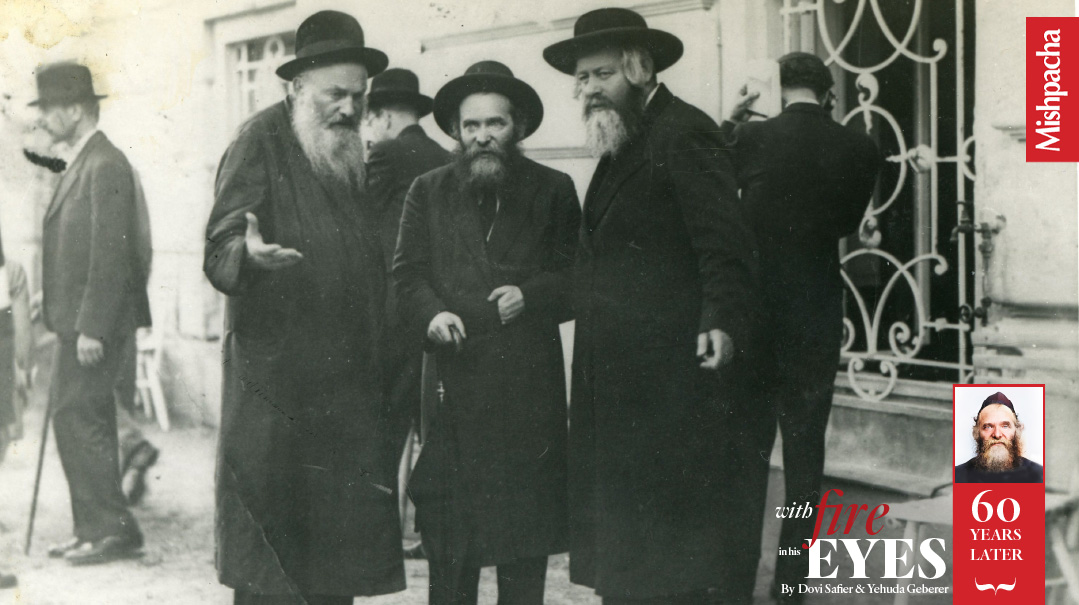
Rav Aharon in conversation with Rav Elchonon Wasserman and Rav Moshe Blau at the 3rd Knessiah Gedolah in Marienbad in 1937
Driving Force
Paradoxically, the passing of the Chofetz Chaim in Elul 1933 provided a new impetus for fundraising. The Vaad HaYeshivos decided to honor its founder with the writing of a sefer Torah in his memory, with the proceeds going toward the support of its affiliate institutions. One of the primary movers behind this initiative was Rav Aharon. He encouraged quick action, as he was concerned that the universal impression left by the Chofetz Chaim’s passing would quickly dissipate. In a letter to Rav Chaim Ozer in December 1933, he explained:
“Time is very limited. We must immediately send out letters requesting all rabbanim and local activists to assist with organizing the campaign. Every passing day is an irrevocable loss to the success of the campaign.”
Rav Aharon even encouraged talented yeshivah students to participate as well, and many of them were sent along with rabbanim on the road for the Chofetz Chaim Torah campaign. Rav Aharon himself was personally involved in commissioning the sefer Torah; he hired a resident of Kletzk, a reliable sofer named Yechezkel Peikuss, to write the Sefer Torah, which was completed in time for the Chofetz Chaim’s second yahrtzeit in 1935.
In hindsight, this relatively overlooked aspect of Rav Aharon’s early leadership served as a prologue to his later efforts to build Torah across the ocean. In interwar Poland, one would be hard pressed to find a rosh yeshivah younger than Rav Aharon Kotler; most of his fellow roshei yeshivah were twice his age. Yet his sense of responsibility for the wider yeshivah world was astonishingly broad. He may have been young, but he was quickly emerging as a driving force of true leadership.
In addition to the respect that Rav Aharon garnered as a rosh yeshivah and Torah leader, he was also occasionally asked to opine on halachic issues. When the Nazis enacted a law in Germany during the 1930s banning traditional shechitah, Rav Yechiel Yaakov Weinberg of Berlin wrote to halachic decisors of the time to elicit their opinions on whether German Jewry could rely on a leniency to stun the animals prior to shechitah. Rav Aharon ruled against this leniency, even for those medically required to eat meat, concerned for the precedent such a dispensation would create.
Rav Yaakov Teitelbaum, leader of the Zeirei Agudah in prewar Vienna and later the rav of Adas Yereim in Kew Gardens, told of a rabbinic gathering in Europe attended by Rav Chaim Ozer. An issue was debated and Rav Aharon, not yet 40, stated his opinion. An elderly rav exclaimed, “Yungerman, sit down. Who are you to speak in the presence of gedolei hador?” Rav Chaim Ozer retorted, “Der yungerman darf men tzu heren vail der nexter dor vet zein oif zein pleitzis — we must pay attention to what this young man has to say, because the next generation will rest on his shoulders!”
This point is further reinforced by a story shared by Rav Aharon Lopiansky. One of the Torah giants of prewar Europe, Rav Mottel Pogromansky, once asked someone to call Rav Aharon on his behalf. When Rav Aharon got on the line, the caller respectfully referred to him as “Kletzker rosh yeshivah.” Rav Mottel exclaimed, “Kletzker rosh yeshivah? The rosh yeshivah! Rav Aharon is much more than just the rosh yeshivah of Kletzk!”
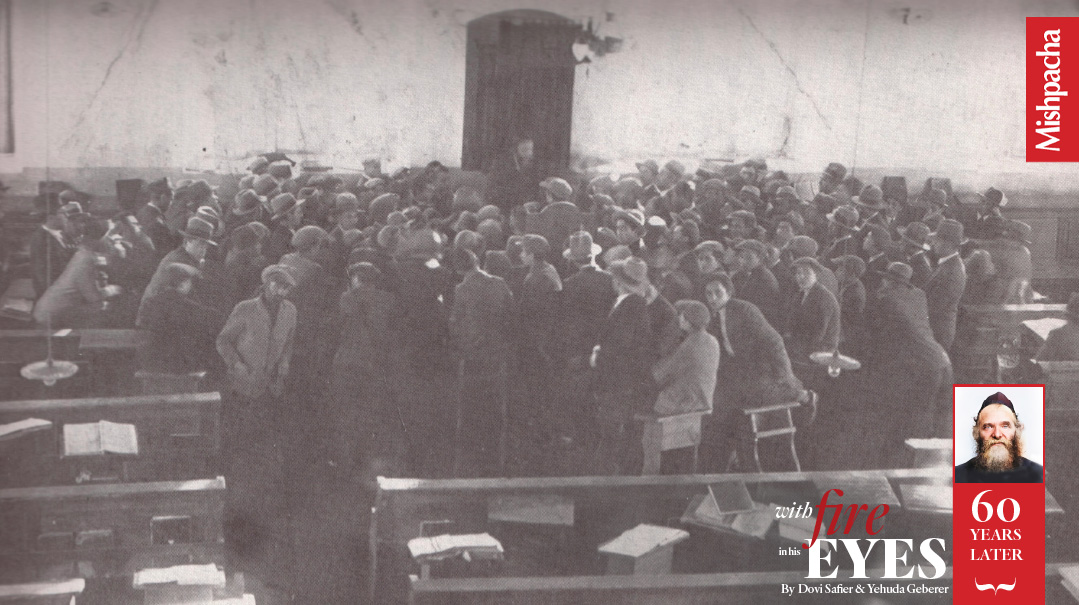

Rav Aharon delivering a shiur in Kletzk
“In listening to Rav Aharon, one always sensed the genius of a deep and penetrating mind arriving at simple conclusions. His approach to learning was creative and vital. In Poland, when there were many yeshivos, people would say, if you would like an approach full of life (lebedeigkeit) then go to Kletzk. True, his shiur consisted of cool logical analysis, but when he spoke, it was a fiery volcano. He gave lie to the myth of the ‘cold Litvak,’ the fire of his great soul manifesting itself in his personality as in his words and deeds”
— Hillel Seidman
Principles Before Politics
Almost from its inception, Rav Aharon was supportive of and active within the Agudas Yisrael political party in Poland. His father-in-law, Rav Isser Zalman, attended the first Knessiah Gedolah in Vienna in 1923, and Rav Aharon himself attended and served in an active role during the crucial third Knessiah Gedolah in Marienbad in 1937.
A report on that Knessiah in Hapardes states that, “Rav [Elchonon] Wasserman, Rav [Aharon] Kotler, Rav [Mordechai] Rottenberg from Antwerp and rabbis from Czechoslovakia and Hungary were in agreement in rejecting any proposal for a Jewish State on either side of the Jordan River, even if it were established as a religious state, because such a regime would be a form of heresy in our faith in the belief in the coming of the Messiah, and especially since it would be built on heresy and desecration of the Name of G-d.”
In the highly politicized atmosphere of interwar Polish Jewry, education — like every other facet of communal life — generally operated within a political affiliation with a specific party and political platform. Due to fundraising concerns, yeshivos generally refrained from overt association of this sort. Rav Aharon, however, had no qualms about taking blunt political positions, even if it meant alienating donors who were Mizrachi supporters.
Decades later a similar issue arose in America, when Rav Aharon led a landmark 1956 ban against participation in mixed-denominational boards of rabbis. In the postwar period, Rav Aharon would be universally recognized as an Agudas Yisrael leader in the United States, and more surprisingly, even in Israel. Following Rav Reuven Grozovsky’s incapacitation in 1952, Rav Aharon assumed the role of chairman of the Moetzes Gedolei Hatorah of Agudath Yisrael of America. He took strong stances on many contemporary issues in both the US and Israel, and elicited anger from supporters with his vocal protests against Israel’s draft law for women as well as the ensuing proposal of Sherut Leumi. Nothing could stand in the way of Rav Aharon’s lifelong pursuit of truth.
(On one of Rav Aharon’s visits to Israel, a Yerushalmi Jew requested a brachah for his young son from Rav Aharon. He acquiesced and blessed him to become a talmid chacham.
“Gib a brocha zohl ehr verrin a kannai — bless him that he become a zealot,” the father pressed, but Rav Aharon demurred, “If he’ll become a talmid chacham he’ll know how to conduct himself.”)
Israeli Agudah politician Rabbi Shlomo Lorincz once asked a man whose lifestyle seemed different from Rav Aharon’s ideals why he was a donor to Beth Medrash Govoha. He answered that Rav Aharon’s personal magnetism was what drew him in, but even more so, he was impressed that Rav Aharon spoke with such enthusiasm and persuasiveness while maintaining his integrity, something he rarely encountered among other rabbis who solicited him.
The Mizrachi leader and Warsaw-based lawyer Zorach Warhaftig, who enjoyed a close relationship with many leading roshei yeshivah including Rav Aharon and would later play a vital role in the rescue of yeshivah students and roshei yeshivah during the war years, recounted in his memoirs his conversation with Rav Aharon regarding one facet among others of his general opposition to Zionism:
“In my many conversations with Rav Aharon Kotler, similar to my ones with Rav Chaim Ozer Grodzinski, I got the impression that they view the study of Torah and the love of Torah as an all-encompassing outlook. They were concerned that love of Zion and Jerusalem would compete for adherents among Jewish youth, and that the latter love would take the place of the former.”
In this regard, Rav Aharon even disputed the position maintained by his own father-in-law. Rav Isser Zalman immigrated to Eretz Yisrael in 1925 and obtained a certificate on behalf of one of his talmidim in the yeshivah who wanted to go as well. When Rav Aharon heard about it, he forbade the talmid from going along, saying, “I forbid you from going! You won’t do well there, there are many apikorsim there.” When the bochur made it clear that he still planned on utilizing the certificate obtained on his behalf by Rav Isser Zalman, Rav Aharon asked him to leave the yeshivah.
As time went on, however, and the security situation in Poland necessitated emigration, Rav Aharon often penned letters requesting certificates to Palestine on behalf of talmidim who requested his assistance. He’d clarify that his fundamental position hadn’t changed; it was rather counterbalanced in individual cases when specific needs arose (such as financial straits, the military draft, etc.).
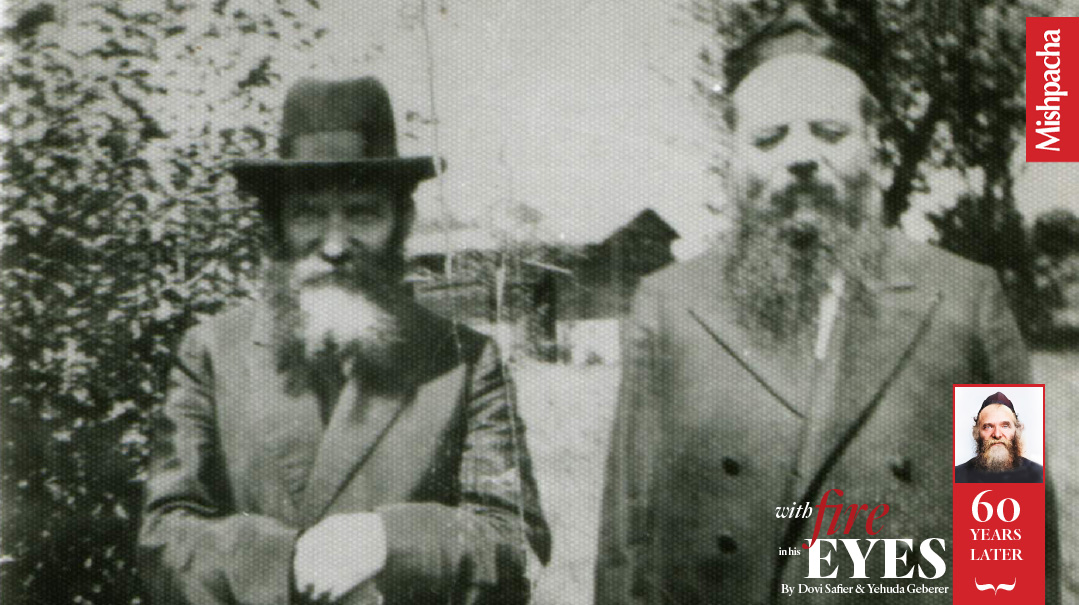

Rav Aharon and Rav Shlomo Heiman in Camp Mesivta.Following Rav Shlomo’s sudden passing in 1944, Rav Aharon volunteered to fill in and say his shiur during the week. After a couple of days Rav Shraga Feivel approached Rav Aharon and proposed that he stay in the position long term. Rav Aharon turned him down. The rest,as they say, is history.
Bitter Days in the Goldeneh Medineh
Even with assistance from the Vaad HaYeshivos and Joint Distribution Committee, meeting the yeshivah’s budget remained a constant challenge. Rav Aharon used to say, “The acronym of Rosh Mesivta is RAM, which when reversed are the letters MAR, which means bitter. It is a great honor to stand at the helm of a packed beis medrash and teach Torah, that is RAM — lofty and elevated. The other side of the coin is the financial struggle, which is MAR — bitter.”
A floundering Polish economy, devaluation of the Polish zloty and the yeshivah’s growing debt meant that Rav Aharon would need to follow the path of other roshei yeshivah and travel abroad to raise funds.
In 1933 he traveled to England and Ireland, but it became apparent that the yeshivah was on the brink of financial collapse. He sensed that he would have no choice but to embark on a journey overseas to the home of the largest and most prosperous Jewish community in the world — the United States of America.
While Rav Meir Shapiro, Rav Boruch Ber Leibowitz, Rav Eliezer Yehuda Finkel, Rav Shimon Shkop and others had conducted fundraising trips to America in the 1920s with varying results, no one had attempted such a journey since the stock market crash of 1929 and ensuing Great Depression. The economy was finally on the upswing, but the depression wouldn’t end until 1939 and funds were still tight for many. Still, Poland’s economy was mired in an even worse depression, and Rav Aharon hoped that Jewish hearts and wallets would open to their needy brothers abroad.
On September 10, 1935, Rav Aharon arrived in New York on the RMS Majestic. In advance of his arrival, The Morgen Journal profiled the Kletzker rosh yeshivah:
“Rav Aharon was already known in his youthful years in Slabodka as the Sislovitzer Illui. …From year to year he grew in his brilliance, and now he is among the giants of the generation. There is no doubt that even the greatest rabbanim and lomdim of New York will be amazed when they will have the zechus to get to know the gaon, Rav Aharon Kotler, the Kletzker Rosh Yeshivah, who is great not only in his Torah learning, but also in worldly knowledge.”
The administrator of Kletzk, Rav Shimon Goder, who would later serve as administrator in Torah Vodaath, had arrived in America three months prior and now joined Rav Aharon during his fundraising appeals.
Rav Aharon spent a Shabbos in East New York as the guest of Rav Tzvi Hirsch Dachowitz, an old friend and respected rav. Rav Aharon addressed the crowd and then Rav Dachowitz announced that for $12, one could cover the expenses of a student for a month. A simple peddler named Tzvi Moshe Cohen stood up and announced that he would pledge $12. He was soon followed by several others, and the appeal was a success.
Immediately after Shabbos, Mr. Cohen rushed to Rav Dachowitz’s home to fulfill his pledge. Rav Dachowitz whispered to Rav Aharon: “You must understand what is going on here! This man is legally blind and hardly has any money to his name. He earns a mere $12 a week as a peddler, and he’s donating his entire weekly salary to the yeshivah.”
Rav Aharon was so moved by this act of mesirus nefesh that he jumped up from behind the table to where Mr. Cohen stood. Thanking him profusely, he blessed him with nachas and greatness in Torah from his children.
His son is the great posek, Rav Dovid Cohen, rav of G’vul Yaavetz in Brooklyn.
On Erev Rosh Hashanah 1937 Rav Aharon wrote to Mr. Cohen: “With a deep sense of gratitude, I recall your love of Torah and generosity, and without taking into account your own dire straits, you donated a number of times more than you were able to. May Hashem consider it a great tzedakah.”
Rav Dovid Cohen related to us a postscript to the story. On December 7, 1941, at the funeral of Rav Dovid Leibowitz, Rav Aharon spotted Mr. Cohen out of the corner of his eye and once again thanked him profusely for his selfless act. It had clearly made a deep impression on Rav Aharon.

When Rav Aharon told Reb Shraga Feivel of his plan to open the yeshivah in Lakewood, without hesitating, Reb Shraga chose some of the Mesivta’s best — including Rav Elya Svei, Rav Yisrael Kanarek, and Rav Yaakov Weisberg — and sent them to Rav Aharon. The roshei yeshivah in Torah Vodaath were understandably upset to lose such prize pupils and complained to Rav Shraga Feivel. He told them unapologetically, “Our task is to cause Torah to flourish, and Rav Aharon cannot be rebbi for students of a lower caliber.” (Photo from the 1947 Torah Umesorah convention in Cleveland)
On the Road
During the course of his 11 months in the United States, Rav Aharon visited locations from Boston to Atlanta, New York to Nebraska. He was introduced to admirers who would become his loyal supporters. Most important was a partnership initiated with Mr. Irving Bunim, who was to emerge as Rav Aharon’s closest confidante for the next three decades.
Whether it was rescue work during the war, building Beth Medrash Govoha, the establishment of Chinuch Atzmai, Torah Umesorah, and almost every endeavor which Rav Aharon would participate and initiate towards the building of postwar Orthodoxy, he’d do so with Irving Bunim at his side.
Other supporters of note were Mrs. Necha Golding and her husband Sam, who hosted Rav Aharon in their New York home. Mrs. Golding also founded the yeshivah’s sisterhood, galvanizing local women to support young men dedicated to Torah learning. At her funeral many years later, Rav Aharon delivered the sole eulogy while crying copious tears. “She was the tzaddeikes hador. There will never be another like her.”
Rav Aharon was also assisted by two young rabbis, Herbert Goldstein and Leo Jung, who made introductions to wealthy congregants and hosted a large tribute event. Another organizer of the New York event was a former Slutzk talmid named Zadok Kapner, a brilliant scholar who had become a successful physician but was still said to be one of the greatest Talmudic minds in America.
During this trip, Rav Aharon spent a significant amount of time in Baltimore. His relative and close friend from Slabodka, Rav Yaakov Yitzchak Ruderman, rosh yeshivah of Ner Yisrael, arranged a number of appointments for Rav Aharon.
At one meeting, Rav Ruderman introduced Rav Aharon as “one of the geniuses of our times, a rosh yeshivah for outstanding pupils.” The man leaned toward Rav Ruderman and requested to speak with him privately.
“Listen,” said the man without the least bit of cynicism. “I like the look of this Jew. Perhaps he’d be willing to become my community’s shochet.”
Rav Ruderman remained bothered by this for quite some time.
The travails of the months Rav Aharon spent on the road are evident in letters he wrote during this time. In a letter penned in Toledo, Ohio, he addresses a query on the subject of “masneh al mah shekasuv baTorah,” and apologizes “because of the great exertion and due to the weakness of my health, as I caught a cold and can’t elaborate.”
He continued: “In Columbus, Ohio $130 dollars was collected; Yesterday evening, we came to Toledo, the rav here Rabbi Nechemia Katz (brother-in-law of Rav Moshe Feinstein) studied at our yeshivah in Slutzk, and of course he is trying to do everything possible…” He also wrote that he considered traveling to Cleveland for the coming Shabbos, but received word that representatives of the Slabodka yeshivah had preceded him. Rav Yechiel Mordechai Gordon of the Lomza Yeshivah was traveling to Detroit, as “it was already scheduled for him earlier, therefore I don’t know yet where we will be for Pesach.”
Rav Aharon arrived in Indianapolis and proposed joining Rav Shmuel Isaac Katz, the local rav, for Shabbos, but the latter (who was clearly unaware of Rav Aharon’s stature) demurred, proposing that Rav Aharon stay at the local community hekdesh (guest hostel), where meshulachim were generally housed. When Rav Aharon insisted, Rav Katz immediately proposed a compromise.
“Although right now I really can’t host you or help you fundraise, I also can’t just absolve myself without doing anything. You know what? I’ll test you and if you pass, you are invited to join us for Shabbos. I can’t refuse a bona fide talmid chacham!”
He then asked Rav Aharon to locate five different passages in Talmud Yerushalmi and Rav Aharon knew them all, earning the right to be Rav Katz’s guest. Rav Aharon later related how much he enjoyed talking in learning with Rav Katz. “He had a mind like the Rogatchover,” Rav Shneur recalled his father saying.
Planting Seeds in American Soil
Much of the difficulties faced by Rav Aharon in America stemmed from the fact that Kletzk was a relatively new yeshivah and didn’t have many alumni serving in prominent roles in America to assist in making connections and collecting multi-year pledges Rav Aharon had received. Letters to Mrs. Necha Golding in the years following the trip beg her to follow up on pledges from others that went unpaid. Senior yeshivos like Mir and Slabodka had alumni networks that greatly assisted with this process. Those rabbis also encouraged advanced American yeshivah students to study in Mir and Slabodka, which generated publicity as well.
The lack of recruiters meant that few Americans came to Kletzk. There were a handful of exceptions, with future rosh yeshivah of Torah Vodaath Rav Gedaliah Schorr the most noteworthy among them. A talmid of Rav Shlomo Heiman in Torah Vodaath, Rav Schorr traveled to Kletzk following his marriage to study under Rav Aharon, remaining there for a year until the American embassy advised him to return home in the summer of 1939. Rav Schorr’s student, Rabbi Nosson Scherman, related that Rav Schorr’s parents had provided the young couple with mattresses for their stay in Kletzk. When the couple arrived and heard that the rosh yeshivah and his rebbetzin slept on straw mattresses, Rav Schorr and his rebbetzin gave their mattresses to the rosh yeshivah instead.
Perhaps the most noteworthy seed planted by Rav Aharon on this trip occurred following his visit to Yeshiva Torah Vodaath. In Rav Shraga Feivel Mendlowitz, Rav Aharon found his kindred spirit, someone who possessed the fire and urge to change the trajectory of Yiddishkeit in the country. He encouraged Rav Shraga Feivel to establish a yeshivah exclusively devoted to Torah learning, sans general studies. Ultimately this dialogue led to the establishment of Bais Medrash Elyon in Monsey.
Rav Aharon suggested three candidates to lead the institution — Rav Yitzchok Hutner, who was then employed in a non-leadership position in Chaim Berlin; Rav Yechezkel Burstyn, rosh yeshivah of Ohr Yisroel in Slabodka and author of Divrei Yechezkel; and his own brother-in-law Rav Yitzchak Meir Patchiner (Ben-Menachem), then a talmid in Slabodka-Chevron. Rav Aharon emphasized that while Rav Yitzchak Meir was his brother-in-law, he was submitting his candidacy strictly based on his merits. He also suggested that Rav Shlomo Heiman deliver an occasional shiur klali and be consulted for his opinion on matters related to the yeshivah.
Rav Aharon returned home prior to Elul of 1936 with a feeling of satisfaction, knowing he had saved the yeshivah in Kletzk from potential closure and could pay up its debts. The challenges continued, however, and prior to Rosh Hashanah he wrote to Rav Yisrael Rosenberg, president of the American Agudath Harabonim and a founder of the rabbinic aid organization Ezras Torah:
You must have heard about the great fire that destroyed a third of Kletzk. It broke out this past eighth of Tammuz. Some yeshivah buildings were damaged, prices of living quarters have risen, and in general everything became more expensive as a result. And of course we have the regular expenses of feeding the yeshivah. We can’t even fix the building because the streets and markets are in the process of being rezoned. We created a basis for the continual support of the yeshivah last year, but now it isn’t sufficient. I know you do a lot, but I’m begging you to do even more considering the circumstances.
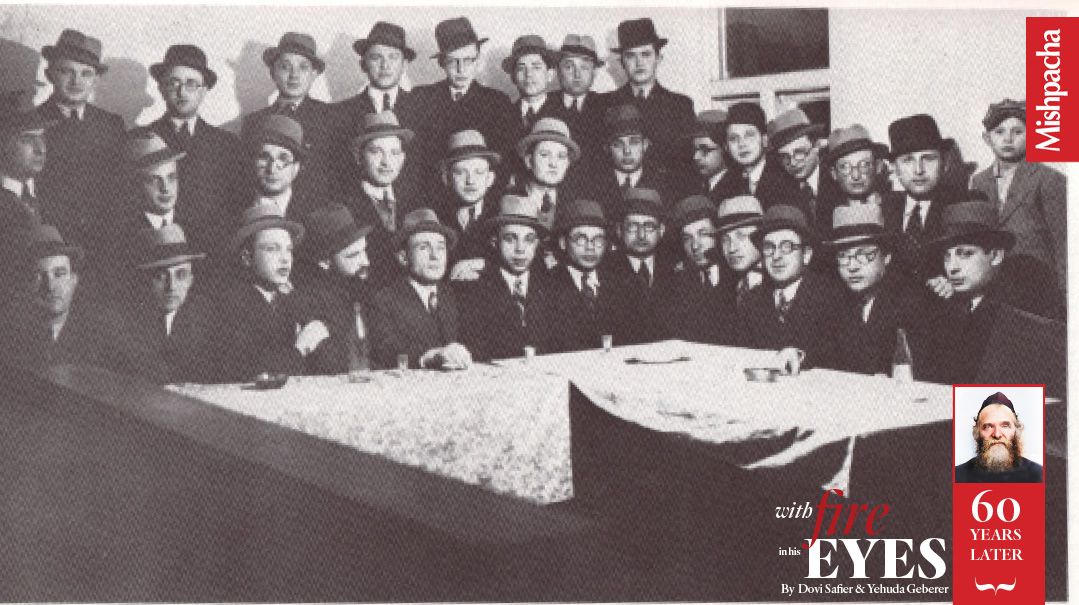

A farewell party in Kletzk for Nochum Uzder (6th from left, bottom row). Other rabbis are (from 1. to r.) middle row: 7th, Shaul Goldman, Brooklyn; 9th, Shmuel Maslow, Brooklyn; 12th, Leib Polak, Denver; top row: 1st, Yaakov Zaretzky, Bnei Brak; 5th, Rav Shneur Kotler, 8th, Alter Pekier
Chapter Three: Escape & rescue
Wartime Refuge
August 23, 1939 was one of the most significant dates in the history of the 20th century. This would be especially true regarding European Jewry. On that day in Moscow, Nazi foreign minister Joachim Von Ribbentrop and Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov signed a non-aggression pact between the two regimes. A secret clause of the agreement was the division of Poland.
A week later the Wehrmacht invaded Poland from the west, while on September 17 the Red Army invaded from the east. By the end of the month Warsaw capitulated, and Poland was divided between the two aggressors.
The bulk of the yeshivos were in Poland’s Kresy region in the east, which fell under the jurisdiction of the Soviets. This put them into a precarious situation, as seminaries of religious instruction were viewed by the atheist communist authorities as hotbeds of counterrevolutionary activity and ran the risk of being forcibly shut or even of arrest and deportation.
Rav Aharon had an acute awareness of the Soviets and their methods. His yeshivah had already escaped the Soviets 18 years earlier from Slutzk, crossing the border illegally into Poland. He knew all too well how dangerous they could be.
Another geopolitical development presented a surprising ray of hope. The city of Vilna and its environs had been incorporated into the Second Polish Republic after World War I. Newly independent Lithuania bemoaned the loss of what they perceived to be their ancient capital, as they temporarily moved the capital to Kovno during the interwar period. Now, upon its invasion of Poland, the Soviet Union annexed eastern Poland including Vilna, and presented Lithuania a doomed offer it couldn’t refuse.
Vilna and its surroundings would be returned to Lithuania — which was neutral during the hostilities — and in return the Soviets would be allowed to establish military bases on Lithuanian territory. Though the Lithuanian government was well aware that the Red Army tended to stay and even expand in any territory under their control, they conceded to the demands of the Soviets. Vilna was to be transferred from Soviet-occupied eastern Poland to independent and neutral Lithuania.
It dawned on thousands of refugees seeking to escape the war zone that anyone in the Vilna district on the date of transfer would cross an international border to a neutral country without any need for documentation or passport. A rush to Vilna commenced, as thousands of refugees clogged the roads in desperation. On October 10, the Lithuanian government signed a mutual assistance treaty with the Soviets, in which Vilna and its environs would be returned to the country in exchange for Soviet military bases on its territory.
On October 28, 1939, the Red Army withdrew from Vilna, and the next day the Lithuanians staged a military parade through the city center. Shortly thereafter, the border between neutral and (somewhat) democratic Lithuania and its neighbors, the Soviet Union and Nazi-occupied Poland, was sealed. Anyone who had made it to Vilna found themselves in relative safety for the time being, in a city teeming with refugees.

“The calm before the storm” Inside the beis medrash in Kletzk during the summer of 1939. Rabbi Alter Pekier is as at right
Come to Vilna!
The titular head of the Vaad HaYeshivos during this fraught period was the aging Rav Chaim Ozer Grodzinski, who carried the Jewish People as a whole and felt a special sense of responsibility towards yeshivah students in particular. Sensing the danger which was to confront the yeshivos under a potential Soviet dominion, he called upon all of the yeshivos to flee posthaste to Vilna.
On October 8, Rav Aharon traveled to Vilna to consult with Rav Chaim Ozer and other roshei yeshivah. A few days later he cabled his family to leave Kletzk immediately together with the entire yeshivah body and administration and head toward Vilna. As the yeshivah left Kletzk for the last time in horse-drawn wagons, they were filled with apprehension — but committed to following Rav Aharon’s instructions.
Upon their arrival at the train station in Baranovich, reports trickled in that a refugee crisis was brewing in Vilna, with overcrowding and food shortages. On Friday afternoon Rebbetzin Chana Perel Kotler advised a group of yeshivah students to wire Rav Aharon and inquire whether to pursue the original plan due to the changing circumstances on the ground.
The reply was not long in coming; the telegram was delivered an hour before the onset of Shabbos: “Yes. Immediately. Take the Friday night train.” The stunned students reluctantly obliged, and following a hasty kiddush in the train station, boarded the Vilna-bound train and arrived there Shabbos morning.
Reunited with his family and talmidim, Rav Aharon sought to move the yeshivah away from the bustle of Vilna and found refuge in the small town of Yanova, north of Kovno, in January 1940. During this time of uncertainty, Rav Aharon launched a new shiur for a select group of students on Seder Zera’im, an area he continued to lecture on upon arriving as a refugee to Manhattan. Funding during this time was provided by both the Joint Distribution Committee, as well as a new organization established at Rav Chaim Ozer’s request to assist the refugee yeshivos continue to function.
Initially named “Emergency Committee for War-Torn Yeshivos,” it was headed by Rav Chaim Ozer’s talmid in America, Rav Eliezer Silver. Later it would be renamed the Vaad Hatzalah.
A traditional Jew from Cincinnati named Dr. Samuel Schmidt was sent to Lithuania by Rav Leizer Silver as an emissary of the nascent group. His letters back home from that trip are an important source towards understanding those tumultuous months. On March 8, 1940, he wrote:
I have just returned from Yanova where the Kletzker Yeshivah is now located. Rav Aharon Kotler is the Rosh Hayeshivah there. He is indeed a most interesting person and considered the greatest Talmudic master of his own age. He is about 48 years, blue smiling eyes, small stature, powerful determination, and penetrating vision. Our talk was limited because of lack of time, two hours in all and half an hour of this we spent in the yeshivah observing the bochurim study. There are about 230 students in this yeshivah, 40 of whom are still in Vilna. Rav Aharon told me of their experience and emotions in leaving Kletzk. It was not so easy to decide upon the move and the pleas of the local Jewish community in Kletzk for them to remain made the task more difficult. Some 45 of the good bochurim were left behind however to be on the watch as it were and it was only about three weeks ago when the Soviets requisitioned their building where they remained on the mishmar and studied until the last minute.
During this time Rav Aharon also traveled often to Kovno, where the foreign embassies were located, to seek a way out for his yeshivah, suspecting that the Lithuanian haven wouldn’t last for long.
He was right. On June 15, 1940 — only eight months after the Kletzk Yeshivah escaped to Vilna — the Lithuanian government caved to a Soviet ultimatum and the Red Army entered the country. On August 3, Lithuania was formally incorporated into the Soviet Union. Once again, the communist noose had tightened and institutions of religious instruction faced an uncertain future.
To make matters worse, another seminal event shook the yeshivah world. Succumbing to a long battle with stomach cancer, Rav Chaim Ozer passed away on August 9. Already in a tenuous situation due to the chaotic war conditions, yeshivah institutions now faced an existential crisis due to the Soviet threat and the death of their patron and undisputed leader.
A rapid Sovietization of Lithuania ensued. Businesses were nationalized, expressions of nationalism were banned, and religious institutions and their leaders were targeted. Kletzk was forced to leave Yanova and split up to evade detection. Dividing into three factions, the largest went to Salock in northern Lithuania, together with Rav Aharon himself. Another contingent, headed by the mashgiach Rav Yosef Leib Nenedick, went to Doshad. A third group of older bochurim went to Duksht.
Rav Aharon intensified his efforts to obtain visas for the entire yeshivah and maintained an active correspondence with activists in the United States such as Rav Yisrael Rosenberg, and pursued any possible lead to save his students.
The Vaad Hatzalah had been able to procure limited above-quota visas designated for clergy, and Rav Aharon was offered one. At this point, it was anathema to him to abandon his talmidim and he politely turned down the offer, still seeking a collective solution to the growing predicament. Rav Isser Zalman also exerted pressure on him to depart, writing to him urgently, “Lama atem yoshvim al har goesh kazeh — Why are you sitting on top of a volcano?”
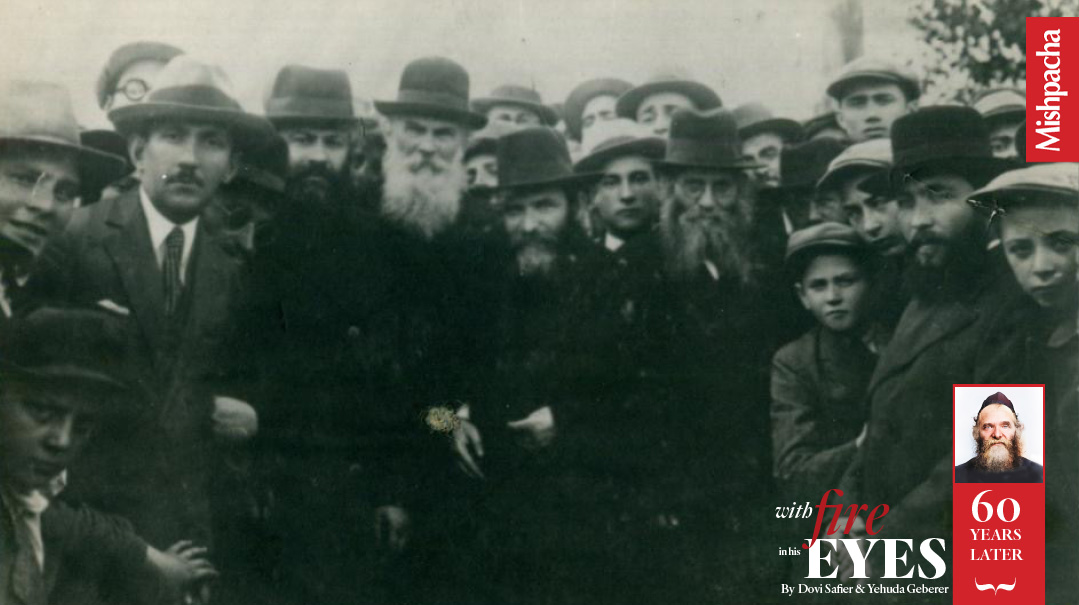

Kletzk Yeshiva in Yanova. The rabbonim at front, from right: Rav Yosef Leib Nenedik, Rav Aharon Kotler and Rav Nachum Baruch Ginzberg of Yanova. Rav Nachum Baruch was the president of the Lithuanian rabbinate and at one point the chairman of the Vaad HaYeshivos. His sefer Mekor Baruch garnered world-acclaim, specifically in the Torah community. He was murdered in the Yanova Ghetto along with his community.
Narrow Window of Escape
Eventually, two developments accentuated the risk factors and paved the way for Rav Aharon’s decision to escape to the United States. In From Kletzk to Siberia, Rabbi Alter Pekier writes:
“On Erev Shabbos, November 8, 1940 the yeshivah’s faithful secretary Reb Berel Starobin was typing Rav Aharon’s chiddushim when agents of the NKVD burst in and began conducting a search. One shoved Reb Berel to the side while the other grabbed the typewriter and a pile of papers. ‘Tell your rabbi that he’d better appear at our headquarters by tonight!’”
“With great trepidation, Rav Aharon walked to the local headquarters. Immediately they began to interrogate him about the ‘suspicious’ contents they’d seized. ‘Those are my commentaries on the Talmud,’ he explained.
“The NKVD agent began to berate him. ‘How ridiculous!! Why do you write such nonsense? Nobody is interested in that stuff anymore!’
“Rav Aharon replied firmly, ‘I won’t allow you to ridicule my religion; the Soviet constitution guarantees freedom of religion.’
“The agent was stunned by his response. ‘You may leave now,’ he said, ‘but we’ll be keeping a close eye on you and your group.’”
Though he’d been released, the intrusion left Rav Aharon with a feeling of uncertainty regarding the future, as well as a sense of urgency. In addition, following the Soviet takeover of Lithuania and the passing of Rav Chaim Ozer, Rav Aharon sensed that the American Vaad Hatzalah had lost its steam. A sense of hopelessness permeated the atmosphere, and he felt that it needed an injection of new energy and motivation in order to galvanize the organization.
These factors made him more amenable to the idea of traveling to the United States on his own, sensing that he could perhaps facilitate the exit of the yeshivah from there, and expedite the process by breathing new life into rescue work.
Utilizing the emergency visa obtained for him by the Vaad Hatzalah, he, his wife, and daughter received their Soviet exit visas and departed Lithuania for Moscow on February 7, 1941. Rav Aharon also managed to include an orphan girl who lived with them named Grunia Winograd on the visa — registering her as an adopted daughter. (His son Rav Shneur had already departed for Palestine using a certificate received from his grandfather Rav Isser Zalman.)
The parting from his beloved talmidim was difficult, though he believed that this was the only way he’d be able to rescue them. Rabbi Alter Pekier continues:
Many rabbis and Jewish leaders from various Lithuanian towns came to Vilna to take leave of Rav Aharon. We, his students, wept bitterly at parting from our teacher. Though we knew that once Rav Aharon was in America our own chances of being able to leave would improve, we felt lost and forsaken. Seventeen months earlier, we had left our parents and families; now we were to lose our spiritual father as well.
Upon arrival in Moscow, Rav Aharon went to the American embassy to receive his travel papers, only to discover that a bureaucratic foul-up had occurred, and the visas had not yet arrived. Zeirei Agudath Israel leader Mike Tress was sitting at his Shabbos table in Williamsburg on Friday night when his doorbell rang. A Western Union messenger handed him an emergency cable, which read:
Came to American Embassy in Moscow to receive Emergency Visa. None waiting. Staff knows nothing about it. Must leave Moscow within 24 hours. Aharon Kotler
Mike rushed straight to the home of Rav Gedaliah Schorr and together they ran to consult with Rav Shlomo Heiman, who instructed them to draft a new visa application immediately. “If I knew how to type, I would do it myself for Rav Aharon!” he told them.
Along with another young activist named Moshe Berger, the duo spent the entire night drafting a new dossier, after which Mike got on a 5:00 a.m. train to Washington and managed to find a sympathetic State Department official to send an authorization letter to the US Embassy in Moscow.
Eventually Rav Aharon made it to Vladivostok, and after a short stint in Kobe, Japan boarded a steamer headed for San Francisco. On Friday, April 11, 1941 (Erev Pesach), Rav Aharon arrived in San Francisco. On Monday, the first day of Chol Hamoed, Rav Aharon took a train east, spending the second part of Yom Tov with Rav Ephraim Epstein (a Vaad Hatzalah leader and the brother of Rav Moshe Mordechai Epstein) in Chicago. Following a quick stop in Cincinnati, he arrived at Penn Station on April 21, 1941.
When he stepped off the platform in midtown Manhattan on that fine spring day, few knew that the Torah landscape of America was about to be transformed forever. Even after this harrowing journey, Rav Aharon wasn’t about to rest on his laurels. His goal had never been to save himself, and with his arrival, he immediately sprang into action. Rav Aharon translated his fiery energy into rescue activities and toward the rebuilding of Europe’s shattered Torah world. The setting and language may have been different, but he would bring the same fire and uncompromising vision to the task.
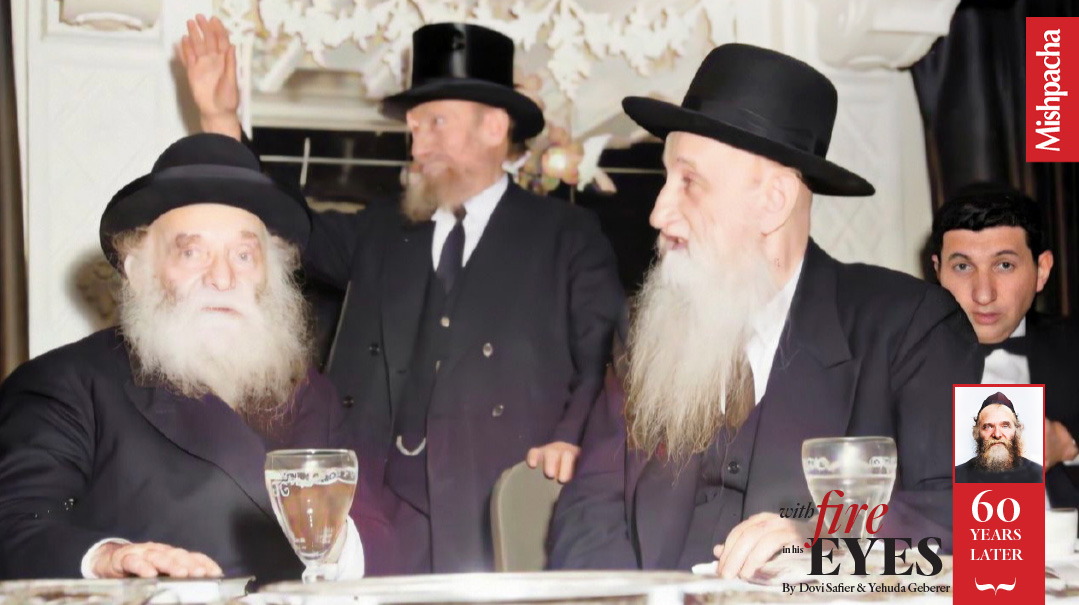

Partners in rescue: Rav Aharon with Rav Eliezer Silver and Rav Avraham Kalmanowitz, who tirelessly led the Vaad Hatzalah rescue attempts during the war years
Father of Wandering Sons
Many books could be — and in fact have been — filled detailing Rav Aharon’s rescue activities during the war years. Many of the stories have become the stuff of legend.
His first order of business upon arrival in the spring of 1941 was to breathe new life into the splintered Vaad Hatzalah organization in order to revitalize its efforts to rescue Torah scholars and yeshivah students. In these efforts he was quite successful, and his charisma, sense of urgency, and boundless energy motivated others as well.
Vaad operative Rabbi Nathan Baruch would never forget his first encounter with Rav Aharon. Shortly after he arrived in New York, Rav Aharon attended a meeting of the Agudath Harabonim and declared, “I am the father of sons who are wandering aimlessly from one place of exile to another, totally abandoned, forsaken. It is my responsibility and yours to save them. I cannot even describe the bitterness and pain we felt upon my departure. Our one consolation is the hope that I will be able to find some help.”
His greatest initial success was to unify the various factions of American Orthodoxy around the mission of rescuing the Eastern European Torah world. Though he was well known for his association with Agudas Yisrael policies and ideology, and for his opposition to Zionism, he was single-handedly responsible for keeping the pro-Zionist Mizrachi faction within the Vaad Hatzalah.
Believing that unity was crucial to rescue, Rav Aharon advised putting aside political and ideological differences and closing ranks among all Orthodox factions to further rescue activities. Vaad Hatzalah was to be an umbrella organization spanning the gamut of American Orthodoxy and included the Agudath Harabonim, Agudas Yisrael, Young Israel, OU and many others. He attempted to work with Reform and secular Jewish leaders and non-Jews as well. When he was criticized for meeting with the leading Reform Rabbi Stephen Wise, Rav Aharon famously declared, “I’d work with the Pope himself, if it would help save the fingernail of one Jewish child.”
Rav Aharon was once berated publicly by an official from a secular organization that likewise engaged in rescue work. The official questioned Rav Aharon, “Whom did you save out of Theresienstadt? They weren’t religious Jews. A lot of them were meshumadim!”
Rav Aharon did not back down. “Who knows why they converted and at what risk they did it?” he countered. “Yisrael af al pi shechatu yisroel hu.”
Left to right: Irving Bunim, Hon. Henry Morgenthau Jr., Hon. John Pehle, Hon. Herbert Tenzer at the December 1945 Vaad Hatzalah Dinner.
Prior to Bunim’s appeal at the dinner he read a newspaper ad for dogs’ winter coats. Each coat, Bunim said, cost a then-enormous $260. “Can you imagine,” he said, his voice choked with emotion, “what our downtrodden brothers in the (DP) camps think of such absurd luxury when they are still struggling to pull together all the broken pieces of their shattered lives?” The silence from the audience rang louder than any verbal response. The appeal netted more than a quarter of a million dollars.
To Rescue the Remainder
On June 22, 1941, the Nazis violated the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact and invaded the Soviet Union. Rav Aharon understood that any attempts to rescue the yeshivah students and Torah scholars in Nazi-occupied Lithuania was now an exercise in futility. Unfortunately, almost all were murdered by the Nazis and their local collaborators.
He knew, however, that many had escaped to the Far East or had been arrested by the Soviets and deported to the Gulag, and he marshaled new energy to focus on saving these last remainders of Europe’s yeshivah world.
Rav Aharon led the efforts of the Vaad Hatzalah to assist those who could manage to immigrate to the United States, and more often to send aid packages and financial assistance to the exiles in Siberia; Kazakhstan; Shanghai, China; and other remote places of dispersion.
Toward the end of 1943, due to the dawning reality of the scope of the Final Solution, the Vaad expanded its rescue operations beyond yeshivah students and Torah scholars to the general rescue of European Jewry. For the remainder of the war, Rav Aharon along with Rav Avraham Kalmanowitz and his close confidante Irving Bunim would lobby diplomats, legislators and anyone who would listen in the corridors of power in Washington to assist in various rescue schemes. Though his pleas generally didn’t find a receptive audience, he and other rescue activists did manage to find an ally in the form of Treasury Secretary Henry Morgenthau Jr.
Irving Bunim shared Rav Aharon’s role in awakening a sleeping giant in his memoirs:
I recall when our great rebbe called on Secretary Henry Morgenthau. At that time Vaad Hatzalah had one million dollars ready for transfer, to be used as barter for Jewish captives who were held in the claws of the accursed German murderers. [Yet] Government policy prohibited the payment of ransom to the enemy. We went to see Secretary Morgenthau in order to get permission to transfer these funds. The Rosh Yeshivah faced Morgenthau across the desk, and Morgenthau told him, “Ransom payments we can’t allow.”
The Rosh Yeshivah, his piercing eyes flashing with fury, spoke emphatically [in Yiddish]. “Tell him, perhaps he is afraid of losing his post; he should be mindful that the life of one single Jew is valued higher than his entire prominent position.”
Morgenthau indignantly replied, “What did he say?”
Afraid of embarrassing him, I generally conveyed there comes a time in a Jew’s life… the Rebbi cut me off and said, “Nein nein Bunim, zugt em vus ich hub gizugt — tell him what I said!”
I did.
When he heard the translation, Morgenthau put his head down for a long time. Then he rose from his armchair and, looking the Rosh Yeshivah straight in the eyes, said, “Tell the rabbi, I am a Jew. Not only would I give up my position, I would sacrifice my life to save my fellow Jews.”
With the eventual formation of the War Refugee Board in January 1944, Rav Aharon and Irving Bunim were able to work with its head John Pehle on several rescue attempts.
Toward the end of the war, Bunim later related, Rav Aharon was told that the Nazis intended to separate American Jewish POWs and presumably have them deported. Rav Aharon contacted Irving Bunim and made plans to petition government officials in Washington to prevent this.
Bunim arrived at Rav Aharon’s house to find him running a fever. He suggested they postpone the trip but Rav Aharon refused, saying, “There are lives at stake and we are going!”
Bunim drafted a memorandum on the train, and Rav Aharon reviewed it at the home of their Washington host, Rav Yehoshua Klavan. “It’s excellent, except the last sentence, which must be removed,” said Rav Aharon. The problematic sentence read, “It’s a sad story that after 20 centuries of oppression, murder, and pogroms, you’ll allow the Nazis’ plans to separate Jewish prisoners of war.”
Rav Aharon thought an official might read that line and conclude, “If they’re being killed for 2,000 years, what’s the big deal if it happens a bit longer?”
The edited memorandum was then presented to David K. Niles, a Jewish advisor to President Roosevelt. Niles contacted General Eisenhower, supreme commander of Allied Forces in Europe. It seems that Eisenhower arranged a broadcast warning the Germans of retribution should they go ahead with this plan.

Following the call of their leaders: When Vaad activist Herman Hollander (not pictured) and his wife Grace learned that there was a possibility that Jewish lives could be “ransomed” from the Nazis, with a sense of alacrity, they sold their hard-earned, newly acquired Brooklyn home, with the proceeds benefiting the life-saving work of the Vaad Hatzalah.
No Sweets or Meat
That same thinking likely prompted Rav Aharon’s decision not to attend the famous Rabbis’ March on Washington in October 1943. Rabbi Nathan Baruch contends that Rav Aharon felt that a public forum was not the proper venue to highlight the plight of the Jews, because he believed the nations of the world reveled in the tragedies befalling the Jewish People. Rav Aharon believed that the appropriate form of activism was for the American Jewish community to aim its frustration directly at elected officials, and that success was more likely through quiet diplomacy conducted behind closed doors.
Rav Simcha Wasserman, a student of Rav Aharon in Kletzk, had arrived in the US and during this period assisted his rosh yeshivah with rescue activities. He never ceased to praise the tireless efforts and the exceptional brilliance of Rav Aharon. Upon hearing that neurologists believe that people have access to only a fraction of their brain’s potential, he declared to his student Rabbi Dr. Dovid Fox, “They never knew Rav Aharon Kotler; every brain cell was full of brilliance!”
Historian Dr. David Kranzler writes of the somber atmosphere that filled the Kotler home during the war years. While their fellow Jews were suffering in Europe, there were no sweets or meat to be found, with the exception of Shabbos.
The Vaad Hatzalah hosted a fundraising dinner in December of 1945 honoring Treasury Secretary Henry Morgenthau and other sympathetic officials. In his landmark address, Morgenthau publicly expressed his admiration for Rav Aharon’s heroics alongside those of Rav Avraham Kalmanowitz and Irving Bunim.
The activities of the Vaad did not cease with the end of the war, because there were still Jews in Europe who desperately needed help. The Vaad worked together with the JDC, in an often-rocky relationship, to provide the bedraggled survivors with kosher food, religious articles, and religious education until they could relocate to established Jewish communities.
Rav Moshe Leibel was a Gerrer chassid who survived the war in the occupied town of Aix-Les-Bains in Southern France where he posed as a doctor while serving as a mohel for the local population. Many young orphans found themselves in Aix-Les-Bains after the war, and Rav Leibel realized that if he didn’t act quickly, he would lose these drifting young Jews to the various secular refugee aid groups. While initially his focus was providing them with kosher food and religious articles, he soon realized that would not suffice and contacted the Vaad Hatzalah for help.
The next day, he received a long-distance phone call from New York. It was Rav Aharon, who immediately initiated rapid-fire questioning regarding the situation on the ground there. After a few minutes, Rav Aharon proclaimed, “You must open a yeshivah — and send all the bills to my home address!”
Named Chachmei Tzarfat after the great Rishonim who had once resided there, the yeshivah started with a group of DPs in Aix-Les-Baines. It eventually became the light that disseminated Torah across France under the leadership of Rav Chaim Chaikin, and yet another initiative of Rav Aharon that wielded a monumental impact.
But even as Rav Aharon continued guiding the Vaad, he also turned his attention to another project: a trailblazing yeshivah in America, now known as America’s Torah capital. Back then, it was known simply as the Lakewood Yeshivah, and Rav Aharon’s leadership role was far from a given.

Rav Yosef Yitzchak Schneerson, the Freidiker Rebbe of Chabad. Following his daring escape from Nazi occupied Poland, he sought out a place to reestablish the Chassidic court of Lubavitch. The Jewish community of Lakewood invited the Rebbe to explore the possibilities of establishing his court there and hosted him for three months in the spring of 1940. Standing (left to right) beginning with Rabbi Nissan Waxman (with mustache): Rabbi Shemaryahu Gurary, Rabbi Shlomo Aron Kazarnovsky, Rabbi Nissan Mindel and Rabbi Chaim Lieberman
Chapter Four: A Vision for America
A Haven Grows in New Jersey
Just weeks after Rav Aharon was born, a small township in central New Jersey received its charter. On March 23, 1892, Lakewood was incorporated by an act of the New Jersey Legislature.
While Lakewood would ultimately become a distinguished seat of Torah in America, its initial growth came courtesy of a well-marketed myth. Before the days of commercial airplane travel, urban dwellers looking to escape the cold winters in New York City would travel to Lakewood, where the temperatures were said to be, on average, more than ten degrees warmer.
Prior to the construction of the Verrazano Bridge and Garden State Parkway, central New Jersey was a distant location from crowded New York City. It wasn’t just the working class who bought into the “warm weather” fallacy and filled the numerous resort hotels that lined the streets along the lake. Some of America’s wealthiest businessmen such as the Rockefellers, Vanderbilts, Goulds, and other titans of industry built mansions on large estates. Along with the influx of revelers came the need for local services and businesses.
It was around the turn of the century that Jews began to arrive in Lakewood to fill these needs. They also began to open small hotels that were marketed as kosher to cater to Jewish clientele. In 1904 the small Jewish community in Lakewood organized when Mr. Charles (Betzalel) Goldstein, an immigrant from Russia who had studied under Rav Leizer Gordon in Telz (Betzalel Day School in Lakewood carried his name), appealed to local residents to open a permanent minyan. Initial quarters were located on top of a Chinese laundry on Fourth Street, and the annual rent was $105.
As the community grew and more Jews began to spend their winters in Lakewood, Charles Goldstein began to envision a permanent home for the budding kehillah. He found an unlikely partner in a former Lakewood postmaster turned real estate and hotel owner, Captain Albert M. Bradshaw.
This former Union army veteran whose obituary claims that he had “done more to benefit Lakewood than any other man” was not, in fact, interested in nurturing religious life. Instead, he wanted to ensure that the shul was built away from the town’s hotels, because he believed that a visible Jewish presence would diminish their value. For a time, Jews were actually forbidden from staying in the two Lakewood hotels he built. In an article about the early history of Lakewood, BMG archivist Rabbi Moshe Rockove pointed out the irony that “one who fought to end slavery in the South would seemingly pursue segregation in his own backyard by drawing a Jewish Mason-Dixon line in his own town.”
Sinister as his motivations may have been, Bradshaw arranged the donation of a plot of land, on the other side of the tracks, at the intersection of Park Avenue and Fourth Street for a synagogue. Goldstein now turned his attention to building the shul and he began to fundraise.
Mrs. Bertha Rayner Frank was born in Baltimore in 1847 into a prestigious Jewish family of German origin. (Her younger brother, Isidor Rayner was one of the first Jews elected to the US Senate.) Shortly after her marriage, she developed an illness that left her crippled. When her wealthy husband passed away in 1906, she vowed to donate her fortune to charity. Her condition had her spending a considerable amount of time in Atlantic City, but when in 1906 one of the hotels she frequented refused to accommodate her niece, telling her that “Jews were not desired as guests,” she decided to make Lakewood her preferred destination.
Charles Goldstein decided to solicit a donation. Mrs. Frank agreed to donate $5,000 and help raise the remaining balance from wealthy friends. By the end of 1907, construction was completed, and Congregation Sons of Israel opened. (This building still stands and is fully functional today — known as “the old shul.” The congregation eventually built a newer location on the corner of 6th and Madison.)
The interwar years saw steady growth of the Jewish population in Lakewood and its environs, including several Jewish chicken farmers in the 1920s. The main attraction in Lakewood remained its hotels, which by then numbered more than 100, many of which catered primarily to Jewish patrons. Rav Moshe Zevulan Margolies (Ramaz) would spend the winter months in Lakewood during his later years. He famously would administer semichah exams while traveling on a horse-drawn sled around the lake. Examinees would know the test went well if they were invited into his home for tea and cookies afterward.
Several visiting European roshei yeshivah spent Shabbos in Lakewood, including Rav Elchonon Wasserman, Rav Shimon Shkop, and Rav Pesach Pruskin. When RIETS began searching for a new home as it grew under the Meitscheter Illui in the 1920s, the Gould Estate (currently Georgian Court University) was one of the locations they considered, before settling on Washington Heights.

The mashgiach, Rav Nosson Meir Wachtfogel (pictured with current rosh yeshivah Rav Malkiel Kotler) was a product of Mir, Kaminetz and Kelm, and was among the founders of the White Plains Kollel. He served as the Mashgiach of Beth Medrash Govoha for a half-century before his passing in 1998
To Recreate What Was
The outbreak of World War II in Europe sent dozens of North American yeshivah students fleeing back home. Many of them were seasoned scholars, having spent nearly a decade in Mir, Kaminetz, Slabodka or Kelm. Several had even gotten married in Europe. Upon returning, they received a stark reminder as to why they had departed America in the first place — the lack of a world class yeshivah faithful to European Torah values. They decided to form a kollel, where they could sequester themselves from the modern currents of “America” and swim in the sea of Torah and mussar as they had in Europe. They named it Beth Medrash Govoha.
Their chosen location was White Plains, New York, an outer suburb of New York in Westchester. The nucleus of the venture included Rav Mordechai Yoffe, Rav Hershel Genauer, Rav Shmuel Shechter, Rav Nosson Wachtfogel, Rav Yitzchok Hoffman, Rav Zeidel Leshinsky, Rav Osher Katz, Rav Simcha Zissel Levovitz, Rav Shachne Zohn, Rav Pesach Cohen, Rav Yisroel Bergstein, Rav Menachem Moore, Rav Hirsch Kaplan, Rav Dovid Hershowitz and others.
Rav Hillel Bishko played an integral role in the kollel’s founding. He arrived in the United States in 1940 at the age of 60, having already spent a lifetime as a great propagator of Torah in Lithuania, where he founded the Tiferes Bochurim network. This noble endeavor created a framework for laborers and merchants to benefit from a Torah environment, replete with batei medrash and shiurim in every locale. The emergence of an experienced administrator for the kollel, helped it gain both legitimacy and financial backing for its initial months.
The Lomza rosh yeshivah, Rav Yechiel Mordechai Gordon, was stranded in the US during the war, and he was hired to serve as rosh kollel. A few months later, he departed and was replaced by the Chofetz Chaim’s son-in-law Rav Mendel Zaks, who soon departed after a short time for Montreal, where he reunited with his mother-in-law, who arrived along with her son and a small nucleus of yeshivah students who fortuitously received Canadian visas. The Lomza Rav, Rav Moshe Shatzkes, also delivered some shiurim to the group.
In 1941 Rav Aharon Kotler arrived in America and expressed his desire to open a yeshivah based upon the structure and values of his yeshivah in Kletzk. The White Plains group sent a delegation led by Rav Mordechai Yaffe to meet with Rav Aharon.
At the time, Rav Aharon was living on the Upper West Side and was completely occupied with rescue work, but still found time to deliver shiurim on Zera’im in his apartment to a small group of Torah Vodaath students, including Rav Avrohom Pam, Rav Elya Moshe Schisgal, Rav Yisrael Kanarek and Rav Simcha Schustal.
He agreed to the proposal to join the White Plains Kollel, subject to three stipulations: The yeshivah would be located out of town, he would retain complete control of spiritual matters, and he’d devote the bulk of his time toward rescue efforts as long as the war continued.

The Building on 6th Street
Rav Aharon turned to his most trusted associate, Irving Bunim, and asked him to help find an ideal location for the yeshivah. Bunim suggested Lakewood, New Jersey, since it was out of town but not too far from New York. Despite the burgeoning vacation industry, it lacked the typical big-city distractions. It had the added bonus of a steady stream of Jewish vacationers who could potentially serve as a fundraising base.
Around the same time, Rav Hillel Bishko came to Lakewood on a fundraising trip for the kollel and delivered a rousing speech, alluding to what the Nazis were currently doing in Europe, dramatically saying, “Dear Friends, I am here to invite you to the funeral and burial of Torah.”
Clearly shaken by these words, Charles Goldstein again took the initiative together with Rabbi Nissan Waxman, an alumnus of European yeshivos and local rabbi. Ironically, Rabbi Waxman had been one of the student delegates representing Mir Yeshiva at the Kletzk groundbreaking in 1929, and had written to Rav Eliezer Yehuda Finkel a few months prior, trying to convince him to reestablish the refugee Mir Yeshiva in Lakewood. This duo was assisted by a local farmer-turned-real estate-agent named Menashe Rabinowitz, and the search commenced for a building to host the yeshivah.
During this time, Rav Aharon refused to commit to Lakewood. Rabbi Waxman described his efforts to convince Rav Aharon to establish a yeshivah in the resort town. “At first, he was reluctant, claiming that it was a resort where people came for pleasure and vanity, and not fit for a spiritual center. But I persuaded him and persevered, visiting him five times until he was convinced.”
Menashe Rabinowitz later recounted how the yeshivah was able to purchase a building at a discounted rate. Following World War I, the Lakewood Township embarked on the construction of a memorial to local soldiers who had perished, inviting famed cantor Yossele Rosenblatt to sing Kel Malei at the consecration. He wasn’t able to make it and Menashe Rabinowitz (who would later lead the Yamim Noraim davening at Beth Medrash Govoha) filled in for him at the event.
When Mr. Rabinowitz approached a potential seller, Matthew J. Sullivan, with a lowball offer to buy 617 6th Street on the yeshivah’s behalf, Sullivan recalled that his interlocutor had sung beautifully at the memorial event two decades earlier and was impressed that he was refraining from charging the accepted realtor’s fee. He agreed to sell his property at a discounted price.
When word spread about the yeshivah’s impending arrival, many of the local residents were suspicious or even dismayed. A neighborhood group organized a petition against the sale, citing potential noise issues in the quiet neighborhood. Supporters of the yeshivah accused the opponents of being biased against “poor war refugees.” The challenges quickly subsided.
Irving Bunim funded the initial purchase with donations from his brother-in-law Isidor Farber as well as his friends Samuel Kaufman and David Shapiro. Still short of $10,000, he personally borrowed the funds. On March 12, 1943, the sale was completed. It was a rare moment of joy for Rav Aharon during the difficult war years.

With his trusted associates Irving & Amos Bunim at a Torah Umesorah dinner in 1956. Torah education is being built, dinner is served and the ever present Mishna Berura never leaves his hand
A Foreign Concept
Once again, the timeless words of Shlomo Hamelech, “The sun rises and the sun sets,” played out. In March, 1944 the Nazis invaded Hungary, and the last bastion of Jewish life in Europe came to a tragic end. Several months before the last Hungarian yeshivos were shuttered, following Pesach of 1943 Beth Medrash Govoha opened its doors in Lakewood with 14 students. A very symbolic number indeed, as this was the exact number of students that had pioneered the launch of the Slutzk Yeshivah almost a half century earlier.
From the start, it was clear that there was little support among potential donors for what was seen as an extreme concept. The departure of Rav Bishko soon after the yeshivah opened compounded the financial strain. Even among those who appreciated Torah and supported local day schools, the idea of full-time post high school Torah study without the goal of semichah was simply preposterous.
To the postwar generation, the practice of Torah lishmah was relegated to history books and serial novels in the Yiddish dailies. An environment of materialism, the relative ease with which immigrants integrated, coupled with the desire for their children to succeed, were factors in this development. College education was seen as a necessity, even among the small American yeshivah community of the 1940s.
Some roshei yeshivah felt that the college challenge could be solved by creating an external college option for yeshivah students. This would fill the need for obtaining the desired college degree while not compromising on the curriculum and attendance of the yeshivah framework. To that end, the American Hebrew Theological University was chartered in 1946 and was set to open in Brooklyn with the endorsement and involvement of prominent roshei yeshivah as a way of contending with the college issue. Rav Aharon’s opposition led to an abandonment of the project. “Rabbosai, from college there will never be a Rav Leib Malin,” he’d tell his students, many of whom faced down resistance from family and friends for studying in a “backward” institution.
Sighet native David Weiss (Halivni) survived the war and arrived in America as an orphan, where he became a student of Rav Yitzchok Hutner at Chaim Berlin. Rav Hutner saw great potential in the young genius and pleaded with him to devote himself exclusively to Torah study. One day, David was asked to drive Rav Aharon from his home in Boro Park to a wedding in Manhattan. Rav Aharon devoted the discussion exclusively to the great need to produce great talmidei chachamim:
“He hammered at the topic that studying Torah is more important than going to college, that the subjects taught in college are inferior in moral content, intellectual rigor, and elevation of spirit. But above all, he argued, there are plenty of people who go to college and so few people who go to yeshivah. He derided the value of secular knowledge by minimizing its achievement.
I could not break out of what sounded to me like a harangue against secular study. I sat quietly and listened, until we passed through a tunnel — I believe it was the Brooklyn-Battery Tunnel, which had been built just a few years before. Rav Aharon stopped talking and looked out the window, to the right and to the left. He bent forward and strained his neck to look backward. “All water,” he said with excitement. “On the top water, below water, and on the side water!”
I couldn’t resist and said, “Rav Aharon, this is what they teach in college.” Without a minute’s hesitation, he retorted, “They already have tunnels.”
Rav Aharon’s message was clear. There were plenty of scientists and engineers. The world will yet survive without another one. But in the wake of the Holocaust, great Torah scholars were an endangered species.
Opponents dubbed this attitude “Kotlerism,” and the lack of sympathy wasn’t limited to the laity. One student of Rav Aharon related how he was berated by a venerated chassidic leader over his choice to study in Lakewood. “If you want to become a rabbi then get semichah,” he was told, “but learning all day without a career goal is nisht ungenumen (unacceptable) in this country!”
Rav Yechiel Perr, rosh yeshivah of Yeshiva Derech Ayson, was a talmid in the fledgling Beth Medrash Govoha during those years. He still recalls a Shabbos visit to the yeshivah by some rabbis who were visiting Lakewood for a convention. As they entered the beis medrash, it was clear they were uncomfortable with what they saw. “Hey look, a Gemara,” one of the rabbis said to his counterpart. “Haven’t seen one of these in a while.”
Few were optimistic that Orthodoxy would flourish in America, and some made helpful suggestions as to how the “Kletzker Yeshivah of Lakewood” could be “improved.” The October 1945 edition of The Orthodox Union, a bimonthly newsletter primarily dedicated to kashrus issues and edited by Rabbi Leo Jung and Dr. Joseph Kaminetsky, featured a letter from a Boro Park resident offering an earnest suggestion to help the yeshivah:
There are quite a number of young men in this country who are motivated by a supreme desire to spend a greater part of their time in the study of Torah. In fact a Kollel at Lakewood, N.J. has been established for this purpose. It is being maintained largely through the efforts of a limited number of people.
The creation of a farm settlement project, where the time of these men could be divided between tilling the soil and the continuation of their studies, would be a step forward in giving them a certain degree of independence and security….
The letter described how the yeshivah-farm could also open a cannery that would produce Kosher for Pesach products and serve as a summer camp as well, and ended on a note of optimism:
…The average worker on the Torah Farm Industrial Project would find more leisure time which may be devoted to the study of Torah, since he need not travel to or from work. Modern machinery and long winter evenings are also conducive in affording more leisure time.
An early student at the yeshivah described how it was such a novelty at the time, that visitors to Lakewood hotels would occasionally peer into the windows of the beis medrash and stare in astonishment at the men avidly learning. After one Shabbos afternoon where they were interrupted several times by gawkers, one student (currently a rosh yeshivah) started flailing his arms like an animal in a zoo until it dawned on the onlookers that perhaps it was inappropriate to be staring as such.
“Father often used to challenge balabatim,” Rav Aharon’s daughter Rebbetzin Sarah Schwartzman told Professor William Helmreich. “At an emergency fundraising meeting, he put it in approximately these words: ‘I don’t want you to misunderstand me; I don’t want to mislead you. There is a need for roshei yeshivos in this country and elsewhere and Lakewood will produce them. There is a need for effective teachers and for the right kind of rabbis and Lakewood will produce these too. There is a need for baleabatim-talmidei chachamim (scholarly laymen) and Lakewood will send them forth. However, the raison d’être of Lakewood is ‘limud haTorah lishmah’ — the study of Torah for its own sake. It is with this understanding, and for this purpose, that I am asking for your support.’”
Rav Aharon shared his worldview with Irving Bunim, pointing to American history as proof. The initial Sephardic immigrants to America in the 1700s built beautiful synagogues, he told Bunim. They came with a value of avodah —tefillah. But the community didn’t flourish.
German Jews arrived in the 19th century and built institutions of chesed, Jewish hospitals, philanthropic organizations such as the Joint — but abandoned traditional Jewish observance.
“Avodah and gemils chasadim are important pillars of Jewish life,” said Rav Aharon, citing Pirkei Avos. “But what sustains the Jewish world is Torah.”

1957 Agudath Harabbonim Convention in Rockaway Park (counterclockwise from bottom center): Rav Chaim Tzvi Kruger, Rav Avraham Yaffen, Rosh Yeshivas Novardok, Rav Meir Cohen, Rav Pinchas Teitz, Rav Dovid Lifshitz, Rav Eliezer Silver, Rav Aharon Kotler, Rav Simcha Elberg, Rav Shimon Morduchovitz and Rav Yaakov Yitzchok Ruderman
A Singular Goal
The early years of the yeshivah witnessed an interesting blend. While the best and brightest of Torah Vodaath and RJJ emerged as the core American talmidim of Rav Aharon, some Kletzk survivors who had spent the war years in the Soviet Union or Shanghai were there for stints as well. This made Beth Medrash Govoha a bridge of sorts, where the yeshivah tradition of Eastern Europe was handed over to a new generation of leaders and Torah scholars.
Though Rav Aharon’s name is most closely linked to Lakewood, the impact of his Torah trailblazing goes far beyond a single yeshivah. He nurtured talmidim who themselves built numerous Torah institutions over the ensuing decades. Yeshivos and Kollelim in Philadelphia, Long Beach, Scranton, Passaic, Stamford, Far Rockaway, St. Louis, Denver, Belle Harbor, Toronto, Boston, Los Angeles, Pittsburgh, as well as several in Brooklyn and other locations throughout the world.
When Rav Shmuel Kamenetsky was encouraged by Rav Aharon to open his yeshivah in Philadelphia, he expressed concern: what kind of chinuch would his children receive in a city that lacked a proper religious educational infrastructure? “If you study Torah lishmah and inculcate that value in others,” Rav Aharon told him, “Hashem will care for your children.” Rav Shmuel often repeats this promise to parents moving to distant locales to spread Torah.
Another talmid, who had been raised in relative comfort, once commented to Rav Aharon that he was having a hard time with the austere kollel lifestyle. Rav Aharon told him, “Your children will not have to worry.” Today his children and grandchildren are major supporters of Torah.
Interestingly enough, though quite a few other postwar yeshivos proudly carried the names of their European antecedents, Rav Aharon never attempted to incorporate Kletzk into the name of the Lakewood yeshivah. In fact, he seldom mentioned it altogether, never evoking the memory of his own yeshivah nor engaging in nostalgia of his decades at its helm. This was presumably partly due to his not having founded Beth Medrash Govoha and therefore not having the “right” to compare it to Kletzk — but there was a subliminal message as well. His grandson Rav Yaakov Eliezer Schwartzman explained it as follows.
As the great activist and builder of America’s postwar Torah world, Rav Aharon had no choice but to remain fixated on the sole goal and vision of generating a Torah revolution in his new country. He surely noticed the hopelessness exuded by so many after the utter devastation of the Holocaust, and concluded that a singular, unshakeable focus on the future was the only path forward. In order to build, create, and motivate a new generation, he could not look back, only forward; he had to kindle, then nurture a fire strong enough, bright enough, and enduring enough to illuminate the entire Torah world.

The Torah world’s “First Family”: A seudas mitzvah at the home of R. Aharon Kotler in America. Right to Left: R. Shneur Kotler (unidentified), R. Aharon Cohen, R. Yaakov Yitzchok Ruderman, R. Aharon Kotler (holding the cup), and R. Yitzchok Chevroni
Cadre of Supporters
Reb Dov Wolowitz recalls driving Rav Aharon to a Moetzes meeting on the Lower East Side. It was a short winter day, and as sunset approached there was still no resolution to the contentious issue under discussion. Mere minutes before sunset, a participant proclaimed, “Rabbosai, Minchah!”
He was interrupted by Rav Yitzchok Hutner. “Nein! Haosek b’mitzvah patur min hamitzvah — someone engaged in a mitzvah is exempt from performing another mitzvah.” All eyes focused on Rav Aharon, the ultimate decisor, who said, “Really, Rav Hutner is right, but what will the balabatim think when they see us skipping Minchah? For that reason we must daven!”
After another deadlocked meeting, a frustrated Rav Hutner told his driver that many of these conferences were not the best use of his time, with endless discussion and little accomplished. “So why does the rosh yeshivah attend these meetings?” the driver asked.
“I go,” Rav Hutner answered, “simply to hear Rav Aharon Kotler utter the word ‘Torah.’”
It was a lesson that many young Americans absorbed, because in addition to producing a cadre of future Torah leaders, Rav Aharon sought to educate a new generation of balabatim about the primacy of supporting Torah and mitzvah observance.
To those faithful balabatim who answered his call of “Torah,” Rav Aharon showed deep appreciation. Rabbi Shaul Robinson shared a powerful story that he heard from a congregant describing Rav Aharon’s deep appreciation for Torah supporters.
The man’s father, a wealthy philanthropist who supported a plethora of causes including Beth Medrash Govoha, experienced a financial reversal. When he lost his money, he stopped hearing from all the rabbis who had solicited him for donations. (Perhaps they did not want to embarrass him; nevertheless, it was a great source of pain.) Except one. Rav Aharon Kotler would call him every Rosh Chodesh. Not for money, but just to say hello.
In November 1954, Rav Aharon delivered a eulogy at the massive funeral of Harry Herskowitz, a devoted layman for whom he had great respect. He mentioned that when Torah Vodaath couldn’t afford to pay its teachers, Mr. Herskowitz conducted an appeal at his daughter’s wedding. “Because of Mr. Herskowitz’s position as the director of the IRS for the Southern District of Manhattan,” Rav Aharon said, “he invited many dignitaries from Washington and New York, some of whom weren’t Jewish, yet he wasn’t ashamed to remind his fellow Jews of their obligation to support Torah.” Incredibly, he halted the dancing until he had raised sufficient funds to keep Torah Vodaath open.
Amos Bunim recalled another eulogy Rav Aharon delivered at the funeral of the great Torah supporter Samuel Kaufman on Chanukah 1960:
When they asked Rav Aharon to be maspid, he said that you’re not permitted to be maspid on Chanukah, but the halachah is that if it’s chacham b’fanav — in the presence of a chacham — it’s permitted. “And I want everybody here to know that here is a man who supported Torah when very few people were willing to support Torah, and therefore I consider him a chacham b’fanav, and I’m going to deliver a hesped.”
What he said was magnificent. “It says ‘s’mach Zevulun b’tzeisecha.’ Simchah can only be achieved in this world if the person grows in Torah. A person supporting Torah, who is Zevulun, doesn’t have the simchah of growing in Torah every day. The Eibishter says, ‘S’mach Zevulun b’tzeisecha’ — Zevulun, when you will leave the world, you will be given this simchah that you missed in This World because you supported Torah.
“You, Mr. Kaufman, were one of the great supporters of Torah, when you leave This World, that simchah will be given to you.”
Rav Aharon actually had two sets of talmidim. One group was in Lakewood and included many students who would emerge as leading roshei yeshivah and builders of Torah. Another was in New York, and they were his students in the art of activism, initiative, responsibility, and leadership.
This second group included people like Irving Bunim and his son Amos, Stephen Klein, Samuel Feuerstein and his son Moses, Mike Tress, Rabbi Moshe Sherer, Marvin Schick, Zev Wolfson, Rabbi Henoch Cohen, Julius Klugman, Ernst Bodenheimer and others. All were driven to action by Rav Aharon’s charisma and his passion for his many causes. They assumed diverse leadership roles in the wider Jewish community, and were inspired by his palpable sense of urgency to act for the benefit of their nation.
Following the 1951 passing of his father-in-law Rav Zelig Fortman (a student of Rav Isser Zalman at Slutzk), Rabbi Moshe Sherer was offered to succeed him as rabbi of the prestigious Congregation Knesseth Israel (the White Shul) in Far Rockaway. The offer was tempting, considering his low salary at the Agudah. He decided to consult with Rav Aharon who told him, “B’shum oifen nisht! Not this shul and not any other shul — I have much bigger plans for you!”
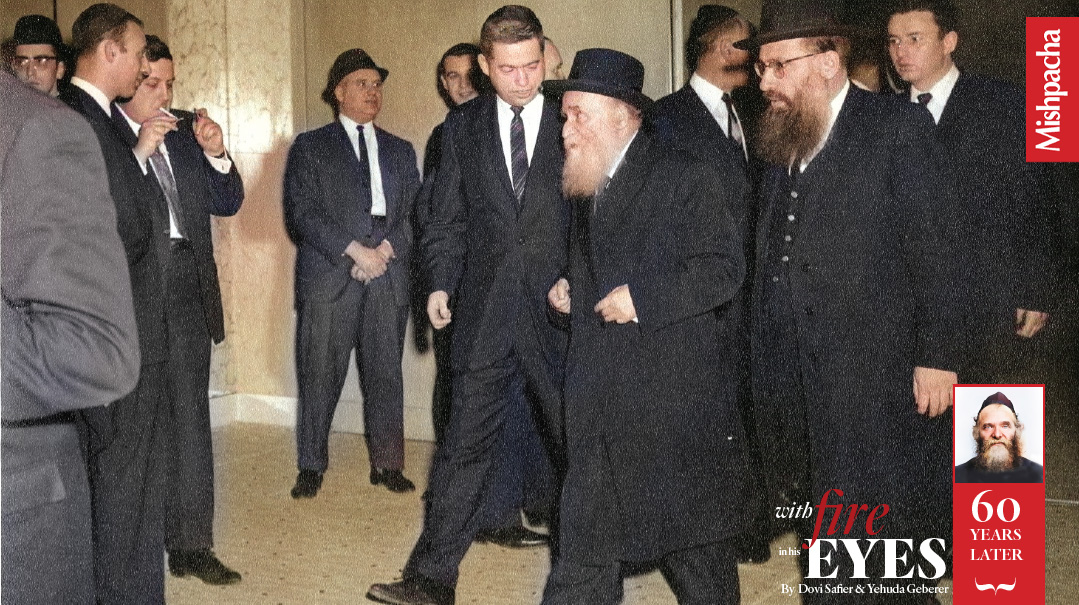


Exiting the Chinuch Atzmai dinner in 1956 (right to left) Agudah MK Rabbi Menachem Porush, Rav Aharon, Zev Wolfson, Julius Klugman (to Mr. Wolfson’s right in background)
Faithful Messenger
Zev Wolfson
Zev Wolfson survived the Holocaust as a teenager in Asiatic Russia and arrived in America with his mother and brother in 1947. Shortly thereafter, he introduced himself to Rav Aharon. “Zev became close to Rav Aharon,” said longtime Chinuch Atzmai chairman Rabbi Henoch Cohen. “Rav Aharon knew his background, and even though he wasn’t polished, he treated him like a son.”
Mr. Wolfson had just turned 25 when he approached Rav Aharon with a bold plan to petition Secretary of State John Foster Dulles via important US Senators, to recommend that Chinuch Atzmai be a recipient of counterpart funds that were being distributed by the US Government at the time.
Senior activists advised Rav Aharon that this plan was a fool’s errand. They claimed it would cause collateral damage to an already frosty relationship between Chinuch Atzmai and the Israeli government, which was vying for the same funding for its own educational and cultural institutions.
But Rav Aharon trusted the young activist who regularly drove him around and helped obtain appointments with donors. He encouraged him to forge ahead with the plan. In a letter to the Brisker Rav, he describes Mr. Wolfson in glowing terms, and in one addressed to Rav Zalman Sorotzkin, he uses the biblical term “Lemichyah shelacho —Hashem sent him as the sustainer.” He finishes by writing, “His suggestions seemed farfetched in my eyes, but I did not ignore them because I know that the perpetuation of the Torah depends on miracles, and his plans came to complete fruition.”
After a couple of years of intense lobbying and enormous hashgachah, Chinuch Atzmai won the coveted allotment. Irving Bunim pointed to that influx of 390,000 pounds as a turning point for Chinuch Atzmai, which resulted in the establishment of 25 new schools.
One would imagine that such an accomplishment would draw endless praise from Rav Aharon. Yet, as is evident from a speech he delivered at a family simchah of Mr. Wolfson’s just weeks before his passing, Rav Aharon, in his wisdom, saw his young charge’s potential to make a continuing and unprecedented impact and encouraged him to do even more:
The plan was, G-d forbid, for a totally different type of education to take hold (in Israel), which would undermine the very existence of a life according to Torah values. And he (Zev) has a tremendous part in this accomplishment (to strengthen Chinuch Atzmai), through lobbying efforts and other means.
Hashem gave him certain strengths and abilities and when one sees results, one cannot let anything stand in the way, and must do whatever is possible to uphold the generation and fight for Yiddishkeit. And since he has the ability, he must persevere! If one is able to accomplish this much, he must do even more.
He therefore has a tremendous obligation. Hashem grants a person the zechus to be able to accomplish, and he has special abilities; he witnessed a special Hashgachah Min Hashamayim to be successful, because now it is possible to achieve success.
One must know, as it is written in the Mesillas Yesharim, that a wise person — for example — has no right to be arrogant. Can a bird boast that it is able to fly to great heights? All other creatures cannot fly. A bird looks around and sees that it was created with wings, thereby it knows that it was endowed with special powers to be able to fly.
[Likewise,] if a Jew puts in effort and is successful, he knows that he cannot take credit for himself, he cannot show off. On the contrary, if you see that you are capable, you must realize that you were given a greater responsibility. Hashem gave you these abilities, he is the one who gave you the power to be successful.
To remove a child from the clutches of heresy and depravity, G-d forbid, is indeed the greatest chesed in the world! To rescue such a child and give him the chance to study Torah, there is no greater chesed in the world! To save a soul — let alone to save Klal Yisrael — it is truly a tremendous zechus! The tremendous zechusim (merits) that you have, is something that you receive reward for in this world. Therefore, we ask Hakodosh Baruch Hu that you should be zocheh to be matzliach and constantly continue your efforts.
Fifty years later, almost to the day, at Mr. Wolfson’s levayah, the rosh yeshivah Rav Malkiel Kotler, declared, “The relationship between my grandfather and Reb Zev was that of a father to his son. Until the last day of his life, Reb Zev lived with a shlichus — a mission that he learnt and felt from Rav Aharon.”
This theme was sustained by Rav Moshe Shapiro, who extolled Mr. Wolfson as the fulfillment of Rav Aharon’s tireless bidding:
Rav Aharon passed away 50 years ago, but his precognition endowed him with the faith that Reb Zev would bring blessing to the Jewish People. In fact, I heard from Reb Zev — understood from him — that all of his activities were the bidding of Rav Aharon. Reb Zev, according to the laws governing “shlichim,” you were in fact the messenger of Rav Aharon. Now that you are with him, fulfill the final law of shlichim, and go to him and tell him, “Rebbi — I have fulfilled your bidding. I have increased Torah among the Jewish People.” He supported thousands of Torah students; they study Torah due to his efforts. Tens of thousands of Jewish children learn due to his energy and in his merit. Thousands of straying children came home in his merit — they returned to the Torah, they became Shabbos observant, they adorn Tefillin, they are occupied with Torah study, and they are building homes of Torah. You can tell Reb Aharon, “I have fulfilled your bidding.”


At the 4th Knessia Gedolah of Agudath Israel in Yerushalayim in 1954 From left: The Imrei Chaim of Vizhnitz, Rav Eliezer Silver, the Beis Yisroel of Ger, Rav Aharon, Mr. Harry Goodman, Moreinu Yaakov Rosenheim, Rav Yitzchok Meir Levin, Rav Elya Meir Bloch (speaking), Rav Tzvi Pesach Frank
Chapter Five: Torah General
The Transatlantic Rosh Yeshivah
During the final decades of his life, Rav Aharon entered a phase of leadership that boggles the mind in terms of its scope and activism. Aside from Vaad Hatzalah of the war and immediate postwar years, he served in a leadership capacity in the Agudath Harabonim and presided over the Moetzes Gedolei Hatorah of Agudas Yisrael. Together with Rav Shraga Feivel Mendlowitz, he was involved in the founding of Torah Umesorah in 1944 and served as chairman of its rabbinical administrative board.
When Rav Aharon visited America in 1935, he observed with sorrow that Baltimore was the only city outside of New York that contained a proper Jewish Day School. Following the founding of Torah Umesorah, he worked in lockstep with Dr. Joseph Kamenetsky, Rabbi Alexander Gross and Rabbi Bernard Goldenberg to found day schools in cities across America, making it clear that he was willing to sacrifice a day saying an intricate shiur on a sugya in Yevamos to ensure that a Jewish child in Minneapolis or Seattle would have the chance to learn the Alef-beis.
Rav Aharon insisted that Rav Boruch Kaplan quit his position at Torah Vodaath and go work alongside wife, Rebbetzin Vichna Kaplan, who had founded the first Bais Yaakov Teachers Seminary in America. “We can find another maggid shiur, but someone who can build a Bais Yaakov? Only you,” Rav Aharon said, well understanding that a Torah revolution would never take hold in America if there was nobody willing to marry yeshivah bochurim and embrace a Torah lifestyle and all that came with it.
Had all his communal responsibilities been merely ceremonial roles, that would have been impressive enough. But mere ceremony was a foreign concept to Rav Aharon. Leadership meant responsibility, responsibility always translated into activism, and activism invariably took the form of launching initiatives, motivating others, and getting the job done.
Even more astounding is that his reach wasn’t limited to the United States. Despite a deep fear of flying, Rav Aharon flew often to Israel throughout the 1950s and early 1960s. Following the passing of Rav Isser Zalman Meltzer in the fall of 1953, Rav Aharon actually succeeded his father-in-law as rosh yeshivah of Etz Chaim in Yerushalayim. Rav Aharon would oftentimes make extended visits to Israel, during which he delivered regular shiurim at Etz Chaim. Rav Aharon traveled by boat on his first trip there in 1945. At a stop in Egypt, Rav Aharon encountered rampant assimilation there and attempted to open a yeshivah.
Rav Aharon attended Moetzes meetings in Israel too, where his opinion was sought on weighty matters involving Israeli elections and politics, leading Rav Leizer Silver to joke at an Agudah Convention that world Jewry had a new kind of leader, “a transatlantic rosh yeshivah.”
And while he supported and interacted with many different types of faithful Jews — enjoying a close relationship with the Kopyczynitzer Rebbe, the Satmar Rav and the Tchebiner Rav — he was unfailingly true to his roots and identity.
Rav Aharon once brought one of his grandsons along with him to a meeting with the Beis Yisrael of Gur. As is traditional in chassidic circles, the Gerrer Rebbe offered the little boy an apple, which he declined saying he wasn’t hungry.
The Gerrer Rebbe, who was not used to being turned down, smiled and quipped, “ah chassid vet er nisht zayn — he will never be a chassid,” at which Rav Aharon quickly instructed his grandson, “Zog amen! Der Rebbe hot gegeiben ah brachah — Say Amen, the Rebbe gave you a brachah!”
Perhaps Rav Aharon’s boldest project was undertaken in the last decade of his life, when he initiated the founding of Chinuch Atzmai in 1953. The history of Chinuch Atzmai and Rav Aharon’s leadership thereof is beyond the scope of this article. Suffice it to say that Rav Aharon believed that the very future of Torah education in Israel was at stake and devoted all his energies to the establishment of an entirely new educational infrastructure from scratch. He asked his close confidante, Mr. Stephen Klein, to oversee the organization, and he embarked on a relentless fundraising campaign.
Rabbi Shlomo Lorincz was present when Beth Medrash Govoah’s financial director Rabbi Yaakov Weisberg informed Rav Aharon that the yeshivah hadn’t paid salaries for five months and suppliers were threatening to stop deliveries. This was due to Rav Aharon devoting all his resources towards Chinuch Atzmai while neglecting his own yeshivah.
“You’re right,” Rav Aharon responded. “I don’t have a proper answer. But what can I do? I’m convinced that Chinuch Atzmai is more important than my own yeshivah.”
This statement is perhaps the best summation of Rav Aharon’s greatness. It seems like a supernatural act. He managed to view even his beloved yeshivah, which carried his hope and vision for the future of American Jewry, through the pure prism of his priorities in building Torah worldwide at any given moment.

Rav Aharon in an animated discussion with Rav Avraham Farbstein while attending the engagement party of of future Mir rosh yeshiva Rav Refoel Shmuelevitz 15 Shvat 1962. The chassan is in the far left and is flanked by his grandfather Rav Leizer Yudel Finkel. One of the great Torah builders of the next generation Rav Nosson Tzvi Finkel is standing on the far right
The Balancing Act
The last two decades of Rav Aharon’s life were marked by a balance between various leadership capacities in the worldwide Torah community and his efforts to mold Beth Medrash Govoha as a premier Torah institution. His dual places of residence serve as a metaphor for this delicate attempt at equilibrium in his twin goals.
During the week he resided in an apartment on 47th Street and 15th Avenue in Boro Park, his center of operations managing, leading, setting policy and fundraising in his capacities as the head of Agudas Yisrael, Chinuch Atzmai, Torah Umesorah, and other communal organizations.
Rebbetzin Chana Perel made the balancing act possible. She could be regularly heard reminding Rav Aharon to take a break to eat, so he’d have strength to learn and engage in his endless activities on behalf of the klal. She asked for nothing for herself, refusing to as much as buy a new dress when she saw that others around her were lacking. When Rav Aharon would take a flight, the rebbetzin would fast until she was assured that he had arrived at his destination.
Not only was she pious and devoted, her wisdom was legendary. She’d often sit outside the dining room where a shiur was taking place and quietly mouth the answers to herself. Rav Aharon was proud of his wife’s comprehensive knowledge of Tanach and would often pose an intricate question to her, smiling when she provided not just one, but two satisfactory answers.
Rav Aharon would only travel to Lakewood for the weekends. During the week, the longtime mashgiach Rav Nosson Wachtfogel ran the yeshivah. Come Shabbos, Rav Aharon would move into the yeshivah, sleeping in the dorm and eating all the Shabbos meals with his beloved talmidim, then personally thanking the cook for the delicious meals. Rav Aharon very much enjoyed zemiros and while not personally blessed with a good voice, he would encourage his talmidim to sing for him, most famously Shlomo Carlebach and Rav Elyakim Getzel Rosenblatt. Rabbi Aaron Twerski relates a story told to him by a fellow talmid, Rav Yekusiel Bittersfeld, who served as Rav Aharon’s attendent one year at the Agudah convention:
We were sitting at the seudah with Rav Mendel Zaks, when Rav Aharon turned to me and said, “Yekusiel, sing a zemer.” Rav Mendel replied, “Zemiros weren’t sung at the table of my father-in-law (the Chofetz Chaim).” Without missing a beat, Rav Aharon said, “Mistameh hut er nit gekent. Yekusiel, zing. — He probably couldn’t. Yekusiel, sing.”
Rav Aharon would deliver two shiurim over the weekend, one on Friday night. Prior to delivering the shiur, Rav Aharon would review it with a few select talmidim.
Several years ago, we had the privilege of visiting Rav Yaakov Schiff, a son-in-law of the Brisker Rav and widely considered to be Rav Aharon’s prime talmid in Lakewood. He shared his reminiscences:
Before Rav Aharon would say the shiur for the entire yeshivah, he would first go over the shiur with a few select talmidim. On occasion, the phone in the room would ring and Rav Aharon would answer the phone and speak with someone, sometimes for quite a long time. After that, he would put down the phone, and continued discussing the shiur, as if there was no interruption, as if he had never stopped. He didn’t have to think over what he was saying, and what he wanted to say now. He continued as if he had never stopped.
Rav Aharon also delivered schmuessen during those years. Rav Leib Rotkin, one of the Kletzkers who survived the war in Siberia and came to Lakewood, recalled that in Europe, Rav Aharon had delivered mussar shmueussen only once a year, on Yom Kippur night. In Lakewood, however, he began delivering them on a regular basis. In summarizing the shmuessen, Rav Nosson Wachtfogel once remarked, “The rosh yeshivah had just one shmuess — the requirement to study Torah, the need to accept upon oneself the yoke of Torah.”
In eulogizing Rav Aharon, Rav Moshe Sherer utilized the Gemara’s description of Rabban Shimon ben Gamliel at the Simchas Beis Hashoeivah celebrations in the Bais Hamikdash. “He would take eight lit torches, throwing one and catching another, without one touching the other” (Succah 53a). The Gemara surely didn’t mean to describe Rabban Shimon ben Gamliel’s physical prowess, rather his ability to simultaneously lead Klal Yisrael in eight different respects, without any one of these areas interfering with the other. Such was the incredible balancing act of Rav Aharon’s leadership of his people in so many ways.”
Rav Michel Shurkin describes with amazement how the “gaon of the generation” would fundraise nonstop, and work around the clock, all so that a Sephardic child in Dimona should learn some Torah. Yet Rav Aharon still felt that his innumerable accomplishments didn’t suffice. He once officiated at the wedding of his talmid Rav Alter Yitzchok Dershowitz in Yerushalayim near the then-Jordanian border. In the middle of the wedding, shells were fired, a large explosion was heard and the room went dark. Rav Aharon took cover under a table, and someone nearby vividly recalled Rav Aharon praying, “Ribbono Shel Olam, ich vill noch leben — I want to live more! Ich hob noch a sach oiftzitohn far Torah — I still have much to accomplish for Torah!”
In 1956, Rav Aharon enlisted Rav Yosef Dov Soloveitchik to serve as guest of honor at the Chinuch Atzmai dinner, (correctly) surmising that his presence and endorsement would draw a large, diverse audience of supporters. The incredibly successful dinner was lionized in a documentary produced by the grandchildren of Irving Bunim entitled, “An Unprecedented Gathering in Support of Torah,” the highlight of which is the keynote address of Rav Soloveitchik:
When I look at Rav Aharon or listen to his words as they flow forth — impatiently, rapidly — when I feel his presence, I feel bound by a sense of achrayus and am reminded of Gedolei Yisrael. There is something within him which compels me to say, as Yosef said about Yehudah, “He’s mibeis abba.” Something in Rav Aharon speaks as I would imagine my great-grandfather Rav Yoshe Ber Brisker once spoke. Something like I would imagine the Chasam Sofer and Rav Akiva Eiger spoke. Uplifting and filled with achrayus. When I talk about Rav Aaron and mibeis abba, I don’t mean just his scholarship, his Torah, but the qualities of a gadol, the warmth and other great middos….
As Rav Soloveitchik extoled praise of Rav Aharon, Rav Aharon tugged on Rav Soloveitchik’s jacket in protest, saying, “nisht emes, nisht emes — it’s not true…”
Rav Aharon once attended a rabbinic conference in Lakewood with the goal of promoting Chinuch Atzmai. Soon after arriving, the speaker began to berate him. One of the students who accompanied Rav Aharon signaled that he was going to try and silence the provoker. When Rav Aharon noticed, he said to the student, “Let him speak, perhaps he’s right.”
Rav Zelig Epstein, rosh yeshivah of Shaar HaTorah, once made a late-night appointment (as was common) with Rav Aharon to discuss an important matter. His son, current Shaar HaTorah rosh yeshivah Rav Kalman Epstein, who was then a young boy, accompanied his father. When they arrived at the Kotler home, the Rebbetzin told them that the Rosh Yeshivah would be arriving late from a trip to Chicago, but if they wished, they could wait. They sat down in the dining room and waited.
It was not until after one o’clock in the morning that Rav Aharon returned home. Rav Kalman recalls that Rav Aharon entered the apartment and immediately made a beeline for his bookshelf and pulled out a Gemara. Completely oblivious to the guests sitting on the other side of the room or the dinner awaiting him on the table, he sat down to learn with incredible passion and energy, as if it were the middle of the day.
Eventually, the Epsteins made their presence known. “That was Rav Aharon,” says Rav Kalman. “He could spend a whole day running around for Klal Yisrael, but his life was coming back to the Gemara.”
Rav Chaim Leib Epstein, Rosh Yeshivah of Zichron Meilech, remembers Rav Aharon preparing for the trip to Lakewood after a tiring week in New York. “He was exhausted, and told his Rebbetzin that he wanted to rest a while before leaving. A few minutes later the Rebbetzin entered the bedroom only to find the Rosh Yeshivah sitting on his bed. Startled, she asked if anything was wrong. The Rosh Yeshivah responded, ‘ich kler, efsher iz dos atzlus — I’m thinking, maybe it’s just laziness!’”

At the wedding of Rabbi Dr. Abraham J. Twerski. Also seen to his left are Rav Shlomo Halberstam of Bobov and Rav Moshe Teitelbaum (the Beirach Moshe) of Satmar
He Was Our General
When Julius Klugman, one of Rav Aharon’s most trusted confidants, was in Israel attending the Fourth Knessiah Gedolah of Agudas Yisrael in 1954, he visited the Brisker Rav. He recalled the Rav referring to Rav Aharon as, “your Rav Aharon.”
“The Brisker Rav was saying that he was ours,” Mr. Klugmann understood. “The Torah community in America had a general and we were his army.”
But it took years for much of American Jewry to truly value Rav Aharon. Rabbi Henoch Cohen, who served as Chinuch Atzmai’s North American director for nearly a half century, related a shocking episode.
“It’s hard to conceive of such a thing now, when the names of Rav Aharon, Rav Moshe, and Rav Yaakov are uttered with such awe, but I was once in a car with the three gedolim en route to a wealthy individual’s home to fundraise for Chinuch Atzmai. ‘Drive slower,’ Rav Aharon told me, ‘so that we arrive after eight. This man has a butler who works until then, but after eight he’ll open the door himself, and hopefully once he sees us, he’ll let us in!’”
Once Rav Aharon concluded a rather unsuccessful day of fundraising by telling his driver Velvel Pearl with a half-smile, “Don’t tell anyone how little money was raised; no one will want to become a rosh yeshivah.”
The extent of Rav Aharon’s mesirus nefesh for America’s Torah future and the steep nature of that uphill battle are neatly encapsulated in a recollection shared by Rabbi Berel Wein.
“I met Rav Aharon Kotler in 1953 when I accompanied my father on a visit to Rabbi Kotler’s then-very small yeshivah in Lakewood, New Jersey. He told my father that he hoped to eventually have over a hundred students.
“I was once in my office when my secretary buzzed me, stating that there was a rabbi calling. Picking up the phone, I heard a voice say in Yiddish, ‘This is Kotler. Last year you gave me ten dollars. I am old and weaker, and I apologize that I cannot come visit you personally. Please send me the ten dollars this year by mail.’
“This is a fairly accurate picture of Orthodox Jewish life in the 1950s. It was a desperate time for Jewry in general, but most certainly for the outnumbered and outgunned Orthodox Jewish community.”
Contrast that with the current era. We live in an age when the amenities of Torah life, institutions and community are taken for granted. Thousands of yungeleit sit and learn all day with hasmadah and zeal championed by supporters, fellow bnei Torah who vie for the opportunity to contribute eye-popping sums to their heroes. How important it is to realize that this is the work of one man.
Look no further than the recent display of kavod haTorah that took place at the Adirei HaTorah event at the Wells Fargo Center in Philadelphia, where a phalanx of modern-day Zevuluns packed the rafters for a chance to pay tribute to the thousands of Yissachars on tiers below them who were the evening’s guests of honor.
Somewhere on the towering dais sat a senior student of Rav Aharon’s from the early days of Beth Medrash Govoha. As he gazed out from his place of honor, he could not help but notice that the endless sea of roshei yeshivah, roshei chaburah and rabbanim sitting alongside him easily outnumbered the entire sum of the postwar Olam HaTorah.
His heart pulsed with joy as 25,000 strong rejoiced in lockstep. Tears rolled down his cheeks as his thoughts turned to his beloved rebbe, Rav Aharon, who just 60 years prior was delivering a shiur before a small group of two dozen charges, eyes on fire as words flowed rapidly from his holy tongue, his entire being seemed consumed in a blissful trance of Torah. He recalled how the small group had been tasked by their general with holding the line, as he promised the imminent arrival of reinforcements.
When the offensive began, the victories came slowly. Another day school, a yeshivah gedolah, kollelim that dotted the fruited plains. Now the entire landscape has changed. America has embraced and nurtured a vision of Torah learning for its own sake. True, there remain new fields to conquer, new struggles to overcome. But Rav Aharon’s vision has prevailed.

At the wedding of Rav Shmuel Kamentsky: (left to right): Rabbis Shaul Goldman, Nachum Goldberg, Berel Peker, Rav Aharon, Chatzkel Horowitz, Paul Z. Levovitz, Shmuel Kamenetsky , Elya Svei, and Rav Dovid Bender.
The knowledge, research and published words of the following distinguished individuals, both past and present, aided in the preparation of this article:
Rabbi Nathan Baruch, Mrs. Chaya Baumwolspiner, Rabbi Eliyahu Beane, Rabbi Asher Bergman, Rabbi Yaakov Bender, Yisroel Besser, Rabbi Amos Bunim, Rabbi Dovid Cohen, Rabbi Henoch Cohen, Rabbi Yitzchok Dershowitz, Rabbi Dov Eliach, Rabbi Shimon Finkelman, Rabbi Dr. Dovid Fox, Shimon Glick, Mrs. Devora Gliksman, Dr. Alex Grobman, Professor William Helmreich, Chaya Sarah Herman, Rabbi Moshe Hillel Hirsch, Rabbi Shimon Hirsch, Rabbi Alexander Hoffman, Rabbi Nosson Kamenetsky, Rabbi Yitzchok Kasnett, Rabbi Dov Katz, Dr. Bentzion Klibansky, Rabbi Moshe Kolodny, The Kotler family, Dr. David Kranzler, Rebbetzin Danielle Leibowitz, Rabbi Nachman Levovitz, Rabbi Aharon Lopiansky, Rabbi Shlomo Lorincz, Reb Shimon Mendlowitz, Symcha Nadborny, The Neuberger family, Rabbi Alter Pekier, Rabbi Yechiel Perr, Rabbi Shaul Robinson, Yonasan Rosenblum, Rabbi Chaim Shlomo Rosenthal, Rabbi Leib Rotkin, Simcha Schecter, Rabbi Marvin Schick, Rabbi Shmaryahu Schulman, Rabbi Gavriel Schuster, Rabbi Nosson Sherman, Rabbi Aaron Sorasky, Zorach Warhaftig, Baruch Wenger, Zev Wolfson, Dov Wolowitz, Rabbi Boruch Ber Yoffe, Pinkas Kletzk, Pinkas Kobryn, Pinkas Slutzk
(Originally featured in Torchbearer, Rav Aharon Kotler Tribute, Issue 941)
Oops! We could not locate your form.